The Multifaceted Interplay between Atrial Fibrillation and Myocardial Infarction: A Review
- PMID: 33430505
- PMCID: PMC7826531
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm10020198
The Multifaceted Interplay between Atrial Fibrillation and Myocardial Infarction: A Review
Abstract
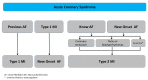
This review was conducted to emphasize the complex interplay between atrial fibrillation (AF) and myocardial infraction (MI). In type 1 (T1) MI, AF is frequent and associated with excess mortality. Moreover, AF after hospital discharge for T1MI is not rare, suggesting the need to improve AF screening and to develop therapeutic strategies for AF recurrence. Additionally, AF is a common trigger for type 2 MI (T2MI), and recent data have shown that tachyarrhythmia or bradyarrhythmia could be a causal factor in, respectively, 13-47% or 2-7% of T2MI. In addition, AF is involved in T2MI pathogenesis as a result of severe anemia related to anticoagulants. AF is also an underestimated and frequent cause of coronary artery embolism (CE), as a situation at risk of myocardial infarction with non-obstructive coronary arteries. AF-causing CE is difficult to diagnose and requires specific management. Moreover, patients with both AF and chronic coronary syndromes represent a therapeutic challenge because the treatment of AF include anticoagulation, depending on the embolic risk, and ischemic heart disease management paradoxically includes antiplatelet therapy.
Keywords: atrial fibrillation; bleeding; chronic coronary syndrome; type 1 and type 2 myocardial infarction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kirchhof P., Benussi S., Kotecha D., Ahlsson A., Atar D., Casadei B., Castella M., Christoph-Diener H., Heidbuchel H., Hendriks J., et al. 2016 ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with EACTS. Eur. Heart J. 2016;37:2893–2962. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehw210. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Thygesen K., Alpert J.S., Jaffe A.S., Chaitman B.R., Bax J.J., Morrow D.A., the Executive Group on behalf of the Joint European Society of Cardiology (ESC) American College of Cardiology (ACC) American Heart Association (AHA) World Heart Federation (WHF) Task Force for the Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction et al. Fourth Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction (2018) Circulation. 2018;138:e618–e651. - PubMed
-
- Chiang C.E., Naditch-Brûlé L., Murin J., Goethals M., Inoue H., O’Neill J., Silva-Cardoso J., Zharinov O., Gamra H., Alam S., et al. Distribution and risk profile of paroxysmal, persistent, and permanent atrial fi-brillation in routine clinical practice insight from the real-life global survey evaluating patients with atrial fibrillation international registry. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2012;5:632–639. doi: 10.1161/CIRCEP.112.970749. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ruff C.T., Giugliano R.P., Braunwald E., Hoffman E.B., Deenadayalu N., Ezekowitz M.D., Camm A.J., Weitz J.I., Lewis B.S., Parkhomenko A., et al. Comparison of the efficacy and safety of new oral anticoagulants with warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation: A meta-analysis of randomised trials. Lancet. 2014;383:955–962. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(13)62343-0. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources