Next-Generation Wearable Biosensors Developed with Flexible Bio-Chips
- PMID: 33430524
- PMCID: PMC7827596
- DOI: 10.3390/mi12010064
Next-Generation Wearable Biosensors Developed with Flexible Bio-Chips
Abstract
The development of biosensors that measure various biosignals from our body is an indispensable research field for health monitoring. In recent years, as the demand to monitor the health conditions of individuals in real time have increased, wearable-type biosensors have received more attention as an alternative to laboratory equipment. These biosensors have been embedded into smart watches, clothes, and accessories to collect various biosignals in real time. Although wearable biosensors attached to the human body can conveniently collect biosignals, there are reliability issues due to noise generated in data collection. In order for wearable biosensors to be more widely used, the reliability of collected data should be improved. Research on flexible bio-chips in the field of material science and engineering might help develop new types of biosensors that resolve the issues of conventional wearable biosensors. Flexible bio-chips with higher precision can be used to collect various human data in academic research and in our daily lives. In this review, we present various types of conventional biosensors that have been used and discuss associated issues such as noise and inaccuracy. We then introduce recent studies on flexible bio-chips as a solution to these issues.
Keywords: biosensor; electrophysiology sensor; flexible electrode; motion artifact noise; wearable biosensor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

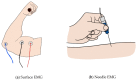

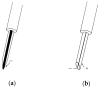


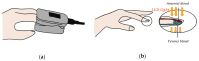
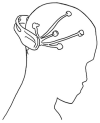




References
-
- Burns A., Greene B.R., McGrath M.J., O’Shea T.J., Kuris B., Ayer S.M., Stroiescu F., Cionca V. SHIMMER™–A wireless sensor platform for noninvasive biomedical research. IEEE Sens. J. 2010;10:1527–1534. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2010.2045498. - DOI
-
- Reisner A., Shaltis P., McCombie D., Asada H. A critical appraisal of opportunities for wearable medical sensors; Proceedings of the 26th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society; San Francisco, CA, USA. 1–5 September 2004; pp. 2149–2152. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

