Vessel wall MRI in ruptured cranial dural arteriovenous fistulas
- PMID: 33430655
- PMCID: PMC8580544
- DOI: 10.1177/1591019920988205
Vessel wall MRI in ruptured cranial dural arteriovenous fistulas
Abstract
Intracranial high-resolution vessel wall MRI (VW-MRI) is an imaging paradigm that is useful in site-of-rupture identification in patients presenting with spontaneous subarachnoid hemorrhage and multiple intracranial aneurysms. Only a handful of case reports describe its potential utility in the evaluation of more complex brain vascular malformations. We report for the first time three patients with ruptured cranial dural arteriovenous fistulas (dAVFs) that were evaluated with high-resolution VW-MRI. The presumed site-of-rupture was identified based on contiguity of a venous ectasia with adjacent blood products and thick, concentric wall enhancement. This preliminary experience suggests a role for high-resolution VW-MRI in the evaluation of ruptured cranial dAVFs, in particular, site-of-rupture identification. It also supports an emerging hypothesis that all spontaneously ruptured, macrovascular lesions demonstrate avid vessel wall enhancement.
Keywords: Dural arteriovenous fistula; magnetic resonance; vessel wall MRI.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
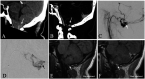
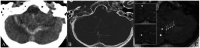
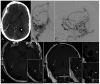
References
-
- Davies MA, TerBrugge K, Willinsky R, et al. The validity of classification for the clinical presentation of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas. J Neurosurg 1996; 85: 830–837. - PubMed
-
- Davies MA, Saleh J, Ter Brugge K, et al. The natural history and management of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulae. Part 1: benign lesions. Interv Neuroradiol 1997; 3: 295–302. - PubMed
-
- Matouk CC, Mandell DM, Günel M, et al. Vessel wall magnetic resonance imaging identifies the site of rupture in patients with multiple intracranial aneurysms: proof of principle. Neurosurgery 2013; 72: 492–496. - PubMed
-
- Omodaka S, Endo H, Niizuma K, et al. Circumferential wall enhancement on magnetic resonance imaging is useful to identify rupture site in patients with multiple cerebral aneurysms. Neurosurgery 2018; 82: 638–644. - PubMed
-
- Texakalidis P, Hilditch CA, Lehman V, et al. Vessel wall imaging of intracranial aneurysms: systematic review and meta-analysis. World Neurosurg 2018; 117: 453–458.e1. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

