Real-world outcomes of different treatment strategies in patients with diabetes and three-vessel coronary disease: a mean follow-up 6.3 years study from China
- PMID: 33430864
- PMCID: PMC7798318
- DOI: 10.1186/s12933-020-01193-3
Real-world outcomes of different treatment strategies in patients with diabetes and three-vessel coronary disease: a mean follow-up 6.3 years study from China
Abstract
Background: Patients with diabetes and triple-vessel disease (TVD) are associated with a high risk of events. The choice of treatment strategies remains a subject of discussion. In the real-world, we aim to compare the outcomes of medical therapy (MT), coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), and percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) treatment strategies in patients with diabetes and TVD.
Methods: A total of 3117 consecutive patients with diabetes and TVD were enrolled. The primary endpoint was all-cause death and the secondary endpoint was major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events (MACCE, composite of all-cause death, myocardial infarction, or stroke).
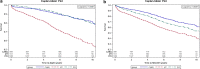
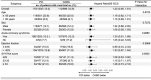
Results: During the mean follow-up of 6.3 ± 2.6 years, 573 (18.4%) deaths and 1094 (35.1%) MACCE occurred. Multivariate analysis showed that PCI (hazard ratio [HR] 0.40, 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.32-0.51) and CABG (HR 0.33, 95% CI 0.26-0.44) were associated with a lower risk of death compared with MT, with no difference between the PCI and CABG groups. When MACCE was the endpoint, PCI (HR 0.71, 95% CI 0.60-0.84) and CABG (HR 0.48, 95% CI 0.39-0.57) had a lower risk than MT. CABG was associated with a significantly lower risk of MACCE compared with PCI (HR 0.67, 95% CI 0.55-0.81), which was mainly attributed a lower risk in myocardial infarction, but a higher risk of stroke.
Conclusions: In this big real-world data and intermediate-term follow-up study, for patients with diabetes and TVD, PCI and CABG were associated with a lower risk of death and MACCE more than MT. The results suggest the importance of appropriate revascularization for diabetic patients with TVD. However, CABG was not associated with a lower risk of death, but with a lower risk of MACCE, compared with PCI. In the future, we perhaps should strengthen comprehensive treatment in addition to PCI or CABG.
Keywords: Diabetes; Prognosis; Treatment strategies; Triple-vessel coronary disease.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors state that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Comment in
-
Treatment strategies in patients with diabetes and three-vessel coronary disease: What should we choose?Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2021 Feb 11;20(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s12933-021-01241-6. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2021. PMID: 33573627 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Donahoe SM, Stewart GC, McCabe CH, Mohanavelu S, Murphy SA, Cannon CP, Antman EM. Diabetes and mortality following acute coronary syndromes. JAMA. 2007;298(7):765–75. - PubMed
-
- Rawshani A, Franzén S, Eliasson B, Svensson AM, Miftaraj M, McGuire DK, et al. Mortality and cardiovascular disease in type 1 and type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2017;376(15):1407–18. - PubMed
-
- Farkouh ME, Domanski M, Sleeper LA, Siami FS, Dangas G, Mack M, et al. Strategies for multivessel revascularization in patients with diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2012;367(25):2375–84. - PubMed
-
- Mohr FW, Morice MC, Kappetein AP, Feldman TE, Ståhle E, Colombo A, et al. Coronary artery bypass graft surgery versus percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with three-vessel disease and left main coronary disease: 5-year follow-up of the randomised, clinical SYNTAX trial. Lancet. 2013;381(9867):629–38. - PubMed
-
- Hakeem A, Garg N, Bhatti S, Rajpurohit N, Ahmed Z, Uretsky BF. Effectiveness of percutaneous coronary intervention with drug-eluting stents compared with bypass surgery in diabetics with multivessel coronary disease: comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical data. Journal of the American Heart Association. 2013;2(4):e000354. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

