Decreased expression of METTL14 predicts poor prognosis and construction of a prognostic signature for clear cell renal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 33430867
- PMCID: PMC7802286
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-020-01738-2
Decreased expression of METTL14 predicts poor prognosis and construction of a prognostic signature for clear cell renal cell carcinoma
Abstract
Background: METTL14, as one of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) related genes, has been found to be associated with promoting tumorigenesis in different types of cancers. This study was aimed to investigate the prognostic value of METTL14 in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC).
Methods: We collected ccRCC patients' clinicopathological parameters information and 13 m6A related genes expression from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database. Univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses were conducted to investigate whether METTL14 could serve as an independent factor correlated with overall survival (OS). Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) was carried out to identify METTL14-related signaling pathways. Moreover, a risk score (RS) was calculated to predict the prognosis of ccRCC. Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) was also utilized to verify the expression of METTL14 in clinical specimens.
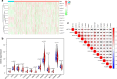
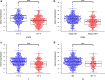
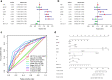
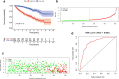
Results: Differently expressed m6A related genes were identified between ccRCC tissues and normal tissues. Therein, METTL14 was lowly expressed in ccRCC tissues and verified by qRT-PCR (all p < 0.01). Survival analysis indicated that high expression of METTL14 was associated with better OS (p = 1e-05). GSEA results revealed that high METTL14 expression was enriched in ERBB pathway, MAPK pathway, mTOR pathway, TGF-β pathway and Wnt pathway. Moreover, METTL14 was proved to be an independent prognostic factor by means of univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses. Nomogram integrating both the METTL14 expression and clinicopathologic variables was also established to provide clinicians with a quantitative approach for predicting survival probabilities of ccRCC. Furthermore, a METTL14-based riskscore (RS) was developed with significant OS (p = 6.661e-16) and increased AUC of 0.856. Besides, significant correlated genes with METTL14 were also provided.
Conclusions: Our results indicated that METTL14 could serve as a favorable prognostic factor for ccRCC. Moreover, this study also provided a prognostic signature to predict prognosis of ccRCC and identified METTL14-related signaling pathways.
Keywords: Clear cell renal cell carcinoma; METTL14; N6-Methyladenosine; Overall survival; Risk score.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020. Cancer J Clin. 2020;70(1):7–30. - PubMed
-
- Yu W, Wang Y, Jiang Y, Zhang W, Li Y. Genetic analysis and clinicopathological features of ALK-rearranged renal cell carcinoma in a large series of resected Chinese renal cell carcinoma patients and literature review. Histopathology. 2017;71(1):53–62. - PubMed
-
- Chen T, Hao YJ, Zhang Y, Li MM, Wang M, Han W, Wu Y, Lv Y, Hao J, Wang L, et al. m(6)A RNA methylation is regulated by microRNAs and promotes reprogramming to pluripotency. Cell Stem Cell. 2015;16(3):289–301. - PubMed
-
- Globisch D, Pearson D, Hienzsch A, Bruckl T, Wagner M, Thoma I, Thumbs P, Reiter V, Kneuttinger AC, Muller M, et al. Systems-based analysis of modified tRNA bases. Angew Chem. 2011;50(41):9739–42. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

