Circular RNAs in body fluids as cancer biomarkers: the new frontier of liquid biopsies
- PMID: 33430880
- PMCID: PMC7798340
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-020-01298-z
Circular RNAs in body fluids as cancer biomarkers: the new frontier of liquid biopsies
Abstract
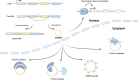
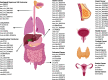
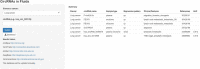
Cancer is a leading cause of death worldwide, particularly because of its high mortality rate in patients who are diagnosed at late stages. Conventional biomarkers originating from blood are widely used for cancer diagnosis, but their low sensitivity and specificity limit their widespread application in cancer screening among the general population. Currently, emerging studies are exploiting novel, highly-accurate biomarkers in human body fluids that are obtainable through minimally invasive techniques, which is defined as liquid biopsy. Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are a newly discovered class of noncoding RNAs generated mainly by pre-mRNA splicing. Following the rapid development of high-throughput transcriptome analysis techniques, numerous circRNAs have been recognized to exist stably and at high levels in body fluids, including plasma, serum, exosomes, and urine. CircRNA expression patterns exhibit distinctly differences between patients with cancer and healthy controls, suggesting that circRNAs in body fluids potentially represent novel biomarkers for monitoring cancer development and progression. In this study, we summarized the expression of circRNAs in body fluids in a pan-cancer dataset and characterized their clinical applications in liquid biopsy for cancer diagnosis and prognosis. In addition, a user-friendly web interface was developed to visualize each circRNA in fluids ( https://mulongdu.shinyapps.io/circrnas_in_fluids/ ).
Keywords: Cancer biomarker; Circular RNA; Liquid biopsy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Collaborators GBDRF Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 79 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks, 1990-2015: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2015. Lancet. 2016;388(10053):1659–1724. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31679-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Schiffman JD, Fisher PG, Gibbs P. Early detection of cancer: past, present, and future. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 2015:57–65. 10.14694/EdBook_AM.2015.35.57. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

