Identification of the active substances and mechanisms of ginger for the treatment of colon cancer based on network pharmacology and molecular docking
- PMID: 33430939
- PMCID: PMC7798235
- DOI: 10.1186/s13040-020-00232-9
Identification of the active substances and mechanisms of ginger for the treatment of colon cancer based on network pharmacology and molecular docking
Abstract
Background and objective: Colon cancer is occurring at an increasing rate and ginger (Zingiber officinale), as a commonly used herbal medicine, has been suggested as a potential agent for colon cancer. This study was aimed to identify the bioactive components and potential mechanisms of ginger for colon cancer prevention by an integrated network pharmacology approach.
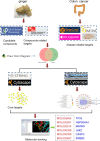
Methods: The putative ingredients of ginger and its related targets were discerned from the TCMSP and Swiss target prediction database. After that, the targets interacting with colon cancer were collected using Genecards, OMIM, and Drugbank databases. KEGG pathway and GO enrichment analysis were performed to explore the signaling pathways related to ginger for colon cancer treatments. The PPI and compound-target-disease networks were constructed using Cytoscape 3.8.1. Finally, Discovery studio software was employed to confirm the key genes and active components from ginger.
Results: Six potential active compounds, 285 interacting targets in addition to 1356 disease-related targets were collected, of which 118 intersection targets were obtained. A total of 34 key targets including PIK3CA, SRC, and TP53 were identified through PPI network analysis. These targets were mainly focused on the biological processes of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling, cellular response to oxidative stress, and cellular response to peptide hormone stimulus. The KEGG enrichment manifested that three signaling pathways were closely related to colon cancer prevention of ginger, cancer, endocrine resistance, and hepatitis B pathways. TP53, HSP90AA1, and JAK2 were viewed as the most important genes, which were validated by molecular docking simulation.
Conclusion: This study demonstrated that ginger produced preventive effects against colon cancer by regulating multi-targets and multi-pathways with multi-components. And, the combined data provide novel insight for ginger compounds developed as new drug for anti-colon cancer.
Keywords: 1-Monolinolein; Colon cancer; GO enrichment; Ginger; KEGG enrichment; Molecular docking.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Exploring active ingredients and mechanisms of Coptidis Rhizoma-ginger against colon cancer using network pharmacology and molecular docking.Technol Health Care. 2024;32(S1):523-542. doi: 10.3233/THC-248046. Technol Health Care. 2024. PMID: 38759074 Free PMC article.
-
[Potential molecular mechanism of Banxia Xiexin Decoction in treatment of colon cancer based on network pharmacology and molecular docking technology].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2020 Dec;45(23):5753-5761. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20201026.401. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 33496116 Chinese.
-
Network-based pharmacology to predict the mechanism of Ginger and Forsythia combined treatment of viral pneumonia.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2021 Sep 15;14(9):964-971. eCollection 2021. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2021. PMID: 34646414 Free PMC article.
-
Study on the mechanism of ErtongKe granules in the treatment of cough using network pharmacology and molecular docking technology.Ann Palliat Med. 2021 Nov;10(11):11415-11429. doi: 10.21037/apm-21-2807. Ann Palliat Med. 2021. PMID: 34872267
-
Network Pharmacology and Experimental Validation to Reveal the Pharmacological Mechanisms of Chongcaoyishen Decoction Against Chronic Kidney Disease.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Mar 31;9:847812. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.847812. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35433831 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacological Effects of Cisplatin Combination with Natural Products in Cancer Chemotherapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 28;23(3):1532. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031532. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163459 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring active ingredients and mechanisms of Coptidis Rhizoma-ginger against colon cancer using network pharmacology and molecular docking.Technol Health Care. 2024;32(S1):523-542. doi: 10.3233/THC-248046. Technol Health Care. 2024. PMID: 38759074 Free PMC article.
-
Integration of network pharmacology and experimental verifications reveals the Bian-Se-Tong mixture can alleviate constipation in STC rats by reducing apoptosis of Cajal cells via activating PI3K-Akt signaling pathway.Heliyon. 2024 Mar 13;10(7):e28022. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e28022. eCollection 2024 Apr 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38586320 Free PMC article.
-
An updated landscape on nanopharmaceutical delivery for mitigation of colon cancer.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Mar;398(3):2107-2125. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03482-0. Epub 2024 Oct 3. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39361171 Review.
-
A New Shapley-Based Feature Selection Method in a Clinical Decision Support System for the Identification of Lung Diseases.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Nov 28;13(23):3558. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13233558. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38066799 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Govindarajan VS. Ginger: chemistry, technology, and quality evaluation: part 1. Crit Rev Food Sci. 1982;17:1–96. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

