An Electronic Tool to Support Patient-Centered Broad Consent: A Multi-Arm Randomized Clinical Trial in Family Medicine
- PMID: 33431386
- PMCID: PMC7800739
- DOI: 10.1370/afm.2610
An Electronic Tool to Support Patient-Centered Broad Consent: A Multi-Arm Randomized Clinical Trial in Family Medicine
Abstract
Purpose: Patients are frequently asked to share their personal health information. The objective of this study was to compare the effects on patient experiences of 3 electronic consent (e-consent) versions asking patients to share their health records for research.
Methods: A multi-arm randomized controlled trial was conducted from November 2017 through November 2018. Adult patients (n = 734) were recruited from 4 family medicine clinics in Florida. Using a tablet computer, participants were randomized to (1) a standard e-consent (standard), (2) an e-consent containing standard information plus hyperlinks to additional interactive details (interactive), or (3) an e-consent containing standard information, interactive hyperlinks, and factual messages about data protections and researcher training (trust-enhanced). Satisfaction (1 to 5), subjective understanding (0 to 100), and other outcomes were measured immediately, at 1 week, and at 6 months.
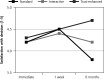
Results: A majority of participants (94%) consented to future uses of their health record information for research. No differences in study outcomes between versions were observed at immediate or 1-week follow-up. At 6-month follow-up, compared with the standard e-consent, participants who used the interactive e-consent reported greater satisfaction (B = 0.43; SE = 0.09; P <.001) and subjective understanding (B = 18.04; SE = 2.58; P <.001). At 6-month follow-up, compared with the interactive e-consent, participants who used the trust-enhanced e-consent reported greater satisfaction (B = 0.9; SE = 1.0; P <.001) and subjective understanding (B = 32.2; SE = 2.6, P <.001).
Conclusions: Patients who used e-consents with interactive research details and trust-enhancing messages reported higher satisfaction and understanding at 6-month follow-up. Research institutions should consider developing and further validating e-consents that interactively deliver information beyond that required by federal regulations, including facts that may enhance patient trust in research.
Keywords: consumer health informatics; electronic health records; health communication; informed consent; trust.
© 2021 Annals of Family Medicine, Inc.
Figures




References
-
- Ohno-Machado L, Alipanah N, Day M, et al. Clinical Data Research Networks, Patient Registries and Patient Powered Research Networks, Taxonomy and Comprehensive Inventories. Patient Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI); 2013.
-
- Califf RM, Robb MA, Bindman AB, et al. Transforming evidence generation to support health and health care decisions. N Engl J Med. 2016; 375(24): 2395-2400. - PubMed
-
- Bayley KB, Belnap T, Savitz L, Masica AL, Shah N, Fleming NS.. Challenges in using electronic health record data for CER: experience of 4 learning organizations and solutions applied. Med Care. 2013; 51(8)(Suppl 3): S80-S86. - PubMed
-
- Federal Policy for the Protection of Human Subjects. In: (OHRP) OfHRP, ed. Vol 45 CFR 46.101. Vol 82, No. 12 ed2018.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
