Cellular and molecular pathobiology of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction
- PMID: 33432192
- PMCID: PMC8574228
- DOI: 10.1038/s41569-020-00480-6
Cellular and molecular pathobiology of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction
Erratum in
-
Publisher Correction: Cellular and molecular pathobiology of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2021 Oct;18(10):735. doi: 10.1038/s41569-021-00516-5. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2021. PMID: 33479518 No abstract available.
Abstract
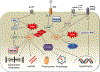
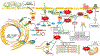
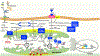
Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) affects half of all patients with heart failure worldwide, is increasing in prevalence, confers substantial morbidity and mortality, and has very few effective treatments. HFpEF is arguably the greatest unmet medical need in cardiovascular disease. Although HFpEF was initially considered to be a haemodynamic disorder characterized by hypertension, cardiac hypertrophy and diastolic dysfunction, the pandemics of obesity and diabetes mellitus have modified the HFpEF syndrome, which is now recognized to be a multisystem disorder involving the heart, lungs, kidneys, skeletal muscle, adipose tissue, vascular system, and immune and inflammatory signalling. This multiorgan involvement makes HFpEF difficult to model in experimental animals because the condition is not simply cardiac hypertrophy and hypertension with abnormal myocardial relaxation. However, new animal models involving both haemodynamic and metabolic disease, and increasing efforts to examine human pathophysiology, are revealing new signalling pathways and potential therapeutic targets. In this Review, we discuss the cellular and molecular pathobiology of HFpEF, with the major focus being on mechanisms relevant to the heart, because most research has focused on this organ. We also highlight the involvement of other important organ systems, including the lungs, kidneys and skeletal muscle, efforts to characterize patients with the use of systemic biomarkers, and ongoing therapeutic efforts. Our objective is to provide a roadmap of the signalling pathways and mechanisms of HFpEF that are being characterized and which might lead to more patient-specific therapies and improved clinical outcomes.
Figures

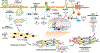
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

