Machine learning reveals bilateral distribution of somatic L1 insertions in human neurons and glia
- PMID: 33432196
- PMCID: PMC8806165
- DOI: 10.1038/s41593-020-00767-4
Machine learning reveals bilateral distribution of somatic L1 insertions in human neurons and glia
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Machine learning reveals bilateral distribution of somatic L1 insertions in human neurons and glia.Nat Neurosci. 2023 Oct;26(10):1833. doi: 10.1038/s41593-023-01438-w. Nat Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37648813 No abstract available.
Abstract
Retrotransposons can cause somatic genome variation in the human nervous system, which is hypothesized to have relevance to brain development and neuropsychiatric disease. However, the detection of individual somatic mobile element insertions presents a difficult signal-to-noise problem. Using a machine-learning method (RetroSom) and deep whole-genome sequencing, we analyzed L1 and Alu retrotransposition in sorted neurons and glia from human brains. We characterized two brain-specific L1 insertions in neurons and glia from a donor with schizophrenia. There was anatomical distribution of the L1 insertions in neurons and glia across both hemispheres, indicating retrotransposition occurred during early embryogenesis. Both insertions were within the introns of genes (CNNM2 and FRMD4A) inside genomic loci associated with neuropsychiatric disorders. Proof-of-principle experiments revealed these L1 insertions significantly reduced gene expression. These results demonstrate that RetroSom has broad applications for studies of brain development and may provide insight into the possible pathological effects of somatic retrotransposition.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests Statement
J.V.M. is an inventor on patent US6150160, is a paid consultant for Gilead Sciences, serves on the scientific advisory board of Tessera Therapeutics Inc. (where he is paid as a consultant and has equity options), and currently serves on the American Society of Human Genetics Board of Directors. C.A.T is or has been a deputy editor for the American Psychiatric Association; an ad hoc consultant for Astellas, Eli Lilly and Lundbeck; a council member for the Brain & Behavior Research Foundation, the Institute of Medicine, the National Alliance on Mental Illness and the National Institute of Mental Health; an organizer for the International Congress on Schizophrenia Research; a consultant for Kaye Scholer; and a member of the advisory board of drug development for Intra-Cellular Therapies.
Figures







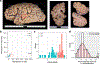

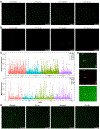
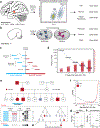


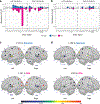

References
-
- Luan DD, Korman MH, Jakubczak JL & Eickbush TH Reverse transcription of R2Bm RNA is primed by a nick at the chromosomal target site: A mechanism for non-LTR retrotransposition. Cell 72, 595–605 (1993). - PubMed
-
- Symer DE et al. Human l1 retrotransposition is associated with genetic instability in vivo. Cell 110, 327–338 (2002). - PubMed
Methods-only References
-
- Stan AD et al. Magnetic resonance spectroscopy and tissue protein concentrations together suggest lower glutamate signaling in dentate gyrus in schizophrenia. Mol. Psychiatry 20, 433–439 (2015). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 MH106883/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH106884/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH106891/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH106876/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH106893/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HG007735/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH100914/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH094740/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH106882/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR025518/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH106892/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH108898/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HD103538/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HG000040/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH106874/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL110952/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

