A trimeric human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 as an anti-SARS-CoV-2 agent
- PMID: 33432247
- PMCID: PMC7895301
- DOI: 10.1038/s41594-020-00549-3
A trimeric human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 as an anti-SARS-CoV-2 agent
Abstract
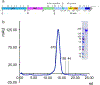
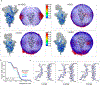
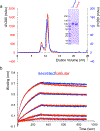
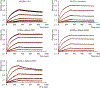
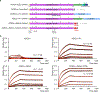
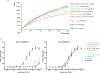
Effective intervention strategies are urgently needed to control the COVID-19 pandemic. Human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) is a membrane-bound carboxypeptidase that forms a dimer and serves as the cellular receptor for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). ACE2 is also a key negative regulator of the renin-angiotensin system that modulates vascular functions. We report here the properties of a trimeric ACE2 ectodomain variant, engineered using a structure-based approach. The trimeric ACE2 variant has a binding affinity of ~60 pM for the spike protein of SARS‑CoV‑2 (compared with 77 nM for monomeric ACE2 and 12-22 nM for dimeric ACE2 constructs), and its peptidase activity and the ability to block activation of angiotensin II receptor type 1 in the renin-angiotensin system are preserved. Moreover, the engineered ACE2 potently inhibits SARS‑CoV‑2 infection in cell culture. These results suggest that engineered, trimeric ACE2 may be a promising anti-SARS-CoV-2 agent for treating COVID-19.
Figures

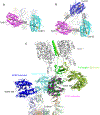


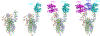
Update of
-
A trimeric human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 as an anti-SARS-CoV-2 agent in vitro.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2020 Sep 18:2020.09.18.301952. doi: 10.1101/2020.09.18.301952. bioRxiv. 2020. Update in: Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2021 Feb;28(2):202-209. doi: 10.1038/s41594-020-00549-3. PMID: 32995768 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
A trimeric human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 as an anti-SARS-CoV-2 agent in vitro.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2020 Sep 18:2020.09.18.301952. doi: 10.1101/2020.09.18.301952. bioRxiv. 2020. Update in: Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2021 Feb;28(2):202-209. doi: 10.1038/s41594-020-00549-3. PMID: 32995768 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Engineered ACE2 receptor traps potently neutralize SARS-CoV-2.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Nov 10;117(45):28046-28055. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2016093117. Epub 2020 Oct 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 33093202 Free PMC article.
-
A super-potent tetramerized ACE2 protein displays enhanced neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 virus infection.Sci Rep. 2021 May 19;11(1):10617. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-89957-z. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34012108 Free PMC article.
-
Contributions of human ACE2 and TMPRSS2 in determining host-pathogen interaction of COVID-19.J Genet. 2021;100(1):12. doi: 10.1007/s12041-021-01262-w. J Genet. 2021. PMID: 33707363 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Two-Way Switch Role of ACE2 in the Treatment of Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia and Underlying Comorbidities.Molecules. 2020 Dec 31;26(1):142. doi: 10.3390/molecules26010142. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33396184 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Structural impact on SARS-CoV-2 spike protein by D614G substitution.Science. 2021 Apr 30;372(6541):525-530. doi: 10.1126/science.abf2303. Epub 2021 Mar 16. Science. 2021. PMID: 33727252 Free PMC article.
-
Foe and friend in the COVID-19-associated acute kidney injury: an insight on intrarenal renin-angiotensin system.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2022 Jan 25;54(1):1-11. doi: 10.3724/abbs.2021002. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2022. PMID: 35130610 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protective neutralizing epitopes in SARS-CoV-2.Immunol Rev. 2022 Sep;310(1):76-92. doi: 10.1111/imr.13084. Epub 2022 May 22. Immunol Rev. 2022. PMID: 35599305 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein.Curr Opin Virol. 2021 Oct;50:173-182. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2021.08.010. Epub 2021 Sep 8. Curr Opin Virol. 2021. PMID: 34534731 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting SARS-CoV-2 and host cell receptor interactions.Antiviral Res. 2023 Feb;210:105514. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2022.105514. Epub 2022 Dec 26. Antiviral Res. 2023. PMID: 36581047 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Shi R et al. A human neutralizing antibody targets the receptor binding site of SARS-CoV-2. Nature 584, 120–124 (2020). - PubMed
Methods-only References:
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

