Prognostic roles of KL-6 in disease severity and lung injury in COVID-19 patients: A longitudinal retrospective analysis
- PMID: 33433006
- PMCID: PMC8013517
- DOI: 10.1002/jmv.26793
Prognostic roles of KL-6 in disease severity and lung injury in COVID-19 patients: A longitudinal retrospective analysis
Abstract
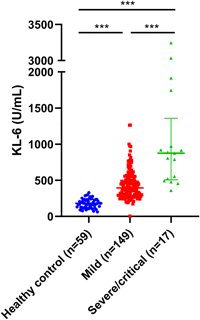
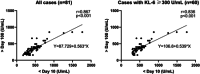
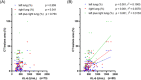
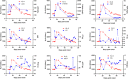
To investigate the dynamic changes of Krebs von den Lungen-6 (KL-6) among patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and the role of KL-6 as a noninvasive biomarker for predicting long-term lung injury, the clinical information and laboratory tests of 166 COVID-19 patients were collected, and a correlation analysis between KL-6 and other parameters was conducted. There were 17 (10.2%, 17/166) severe/critical and 149 (89.8%, 149/166) mild COVID-19 patients in our cohort. Serum KL-6 was significantly higher in severe/critical COVID-19 patients than in mild patients (median 898.0 vs. 451.2 U/ml, p < .001). KL-6 was next confirmed to be a sensitive and specific biomarker for distinguishing mild and severe/critical patients and correlate to computed tomography lung lesions areas. Serum KL-6 concentration during the follow-up period (>100 days postonset) was well correlated to those concentrations within 10 days postonset (Pearson r = .867, p < .001), indicating the prognostic value of KL-6 levels in predicting lung injury after discharge. Finally, elevated KL-6 was found to be significantly correlated to coagulation disorders, and T cells subsets dysfunctions. In summary, serum KL-6 is a biomarker for assessing COVID-19 severity and predicting the prognosis of lung injury of discharged patients.
Keywords: COVID-19; KL-6; lung injury; prognosis.
© 2021 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interests.
Figures
References
-
- https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situatio.... Accessed October 30, 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

