Interactions Between Enhanced Polygenic Risk Scores and Lifestyle for Cardiovascular Disease, Diabetes, and Lipid Levels
- PMID: 33433237
- PMCID: PMC7887077
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCGEN.120.003128
Interactions Between Enhanced Polygenic Risk Scores and Lifestyle for Cardiovascular Disease, Diabetes, and Lipid Levels
Abstract
Background: Both lifestyle and genetic factors confer risk for cardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetes, and dyslipidemia. However, the interactions between these 2 groups of risk factors were not comprehensively understood due to previous poor estimation of genetic risk. Here we set out to develop enhanced polygenic risk scores (PRS) and systematically investigate multiplicative and additive interactions between PRS and lifestyle for coronary artery disease, atrial fibrillation, type 2 diabetes, total cholesterol, triglyceride, and LDL-cholesterol.
Methods: Our study included 276 096 unrelated White British participants from the UK Biobank. We investigated several PRS methods (P+T, LDpred, PRS continuous shrinkage, and AnnoPred) and showed that AnnoPred achieved consistently improved prediction accuracy for all 6 diseases/traits. With enhanced PRS and combined lifestyle status categorized by smoking, body mass index, physical activity, and diet, we investigated both multiplicative and additive interactions between PRS and lifestyle using regression models.
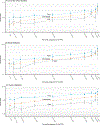
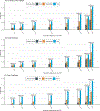
Results: We observed that healthy lifestyle reduced disease incidence by similar multiplicative magnitude across different PRS groups. The absolute risk reduction from lifestyle adherence was, however, significantly greater in individuals with higher PRS. Specifically, for type 2 diabetes, the absolute risk reduction from lifestyle adherence was 12.4% (95% CI, 10.0%-14.9%) in the top 1% PRS versus 2.8% (95% CI, 2.3%-3.3%) in the bottom PRS decile, leading to a ratio of >4.4. We also observed a significant interaction effect between PRS and lifestyle on triglyceride level.
Conclusions: By leveraging functional annotations, AnnoPred outperforms state-of-the-art methods on quantifying genetic risk through PRS. Our analyses based on enhanced PRS suggest that individuals with high genetic risk may derive similar relative but greater absolute benefit from lifestyle adherence.
Keywords: atrial fibrillation; cardiovascular disease; coronary artery disease; healthy lifestyle; triglycerides.
Figures


References
-
- Benjamin EJ, Muntner P, Alonso A, Bittencourt MS, Callaway CW, Carson AP, Chamberlain AM, Chang AR, Cheng S, Das SR, et al., American Heart Association Council on Epidemiology and Prevention Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2019 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2019;139:e56–e528. - PubMed
-
- Arnett DK, Blumenthal RS, Albert MA, Buroker AB, Goldberger ZD, Hahn EJ, Himmelfarb CD, Khera A, Lloyd-Jones D, McEvoy JW, et al. 2019 ACC/AHA Guideline on the Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2019;140:e596–e646. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

