Induced pluripotent stem cell technology for spinal cord injury: a promising alternative therapy
- PMID: 33433463
- PMCID: PMC8323703
- DOI: 10.4103/1673-5374.303013
Induced pluripotent stem cell technology for spinal cord injury: a promising alternative therapy
Abstract
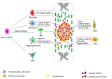
Spinal cord injury has long been a prominent challenge in the trauma repair process. Spinal cord injury is a research hotspot by virtue of its difficulty to treat and its escalating morbidity. Furthermore, spinal cord injury has a long period of disease progression and leads to complications that exert a lot of mental and economic pressure on patients. There are currently a large number of therapeutic strategies for treating spinal cord injury, which range from pharmacological and surgical methods to cell therapy and rehabilitation training. All of these strategies have positive effects in the course of spinal cord injury treatment. This review mainly discusses the problems regarding stem cell therapy for spinal cord injury, including the characteristics and action modes of all relevant cell types. Induced pluripotent stem cells, which represent a special kind of stem cell population, have gained impetus in cell therapy development because of a range of advantages. Induced pluripotent stem cells can be developed into the precursor cells of each neural cell type at the site of spinal cord injury, and have great potential for application in spinal cord injury therapy.
Keywords: axon regeneration; cell therapy; functional recovery; induced pluripotent stem cell; mesenchymal stem cell; neural cells; neural precursor cell; neural stem cell; remyelination; spinal cord injury; stem cells.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures


References
-
- Ahuja CS, Nori S, Tetreault L, Wilson J, Kwon B, Harrop J, Choi D, Fehlings MG. Traumatic spinal cord injury-repair and regeneration. Neurosurgery. 2017;80:S9-S22. - PubMed
-
- Anderson KD, Guest JD, Dietrich WD, Bartlett Bunge M, Curiel R, Dididze M, Green BA, Khan A, Pearse DD, Saraf-Lavi E, Widerstrom-Noga E, Wood P, Levi AD. Safety of autologous human schwann cell transplantation in subacute thoracic spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma. 2017;34:2950–2963. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

