Inhibition of nitric oxide synthase aggravates brain injury in diabetic rats with traumatic brain injury
- PMID: 33433486
- PMCID: PMC8323706
- DOI: 10.4103/1673-5374.303035
Inhibition of nitric oxide synthase aggravates brain injury in diabetic rats with traumatic brain injury
Abstract
Studies have shown that hyperglycemia aggravates brain damage by affecting vascular endothelial function. However, the precise mechanism remains unclear. Male Sprague-Dawley rat models of diabetes were established by a high-fat diet combined with an intraperitoneal injection of streptozotocin. Rat models of traumatic brain injury were established using the fluid percussion method. Compared with traumatic brain injury rats without diabetic, diabetic rats with traumatic brain injury exhibited more severe brain injury, manifested as increased brain water content and blood-brain barrier permeability, the upregulation of heme oxygenase-1, myeloperoxidase, and Bax, the downregulation of occludin, zona-occludens 1, and Bcl-2 in the penumbra, and reduced modified neurological severity scores. The intraperitoneal injection of a nitric oxide synthase inhibitor N(5)-(1-iminoethyl)-L-ornithine (10 mg/kg) 15 minutes before brain injury aggravated the injury. These findings suggested that nitric oxide synthase plays an important role in the maintenance of cerebral microcirculation, including anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidative stress, and anti-apoptotic activities in diabetic rats with traumatic brain injury. The experimental protocols were approved by the Institutional Animal Care Committee of Harbin Medical University, China (approval No. ky2017-126) on March 6, 2017.
Keywords: apoptosis; blood-brain barrier; brain edema; diabetes mellitus; inflammation; injury; neurological function; nitric oxide synthase; traumatic brain injury.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures



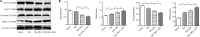
References
-
- Abou-El-Hassan H, Dia B, Choucair K, Eid SA, Najdi F, Baki L, Talih F, Eid AA, Kobeissy F. Traumatic brain injury, diabetic neuropathy and altered-psychiatric health: The fateful triangle. Med Hypotheses. 2017;108:69–80. - PubMed
-
- Alvis-Miranda HR, Navas-Marrugo SZ, Velasquez-Loperena RA, Adie-Villafañe RJ, Velasquez-Loperena D, Castellar-Leones SM, Alcala-Cerra G, Pulido-Gutiérrez JC, Rodríguez-Conde JR, Moreno-Moreno MF, A MR, Moscote-Salazar LR. Effects of glycemic level on outcome of patients with traumatic brain injury: a retrospective cohort study. Bull Emerg Trauma. 2014;2:65–71. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bosarge PL, Shoultz TH, Griffin RL, Kerby JD. Stress-induced hyperglycemia is associated with higher mortality in severe traumatic brain injury. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2015;79:289–294. - PubMed
-
- Brizuela M, Blizzard CA, Chuckowree JA, Pitman KA, Young KM, Dickson T. Mild traumatic brain injury leads to decreased inhibition and a differential response of calretinin positive interneurons in the injured cortex. J Neurotrauma. 2017;34:2504–2517. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

