DDAH2 (-449 G/C) G allele is positively associated with leukoaraiosis in northeastern China: a double-blind, intergroup comparison, case-control study
- PMID: 33433489
- PMCID: PMC8323672
- DOI: 10.4103/1673-5374.303037
DDAH2 (-449 G/C) G allele is positively associated with leukoaraiosis in northeastern China: a double-blind, intergroup comparison, case-control study
Abstract
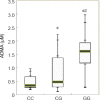
Cerebrovascular endothelial dysfunction is involved in the progression of leukoaraiosis. Asymmetric dimethylarginine is a competitive inhibitor of nitric oxide, which is highly expressed in patients with leukoaraiosis. Dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase (DDAH) is a hydrolytic enzyme that is primarily responsible for eliminating asymmetric dimethylarginine, and it plays a role in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. The DDAH2 subtype is expressed in organs rich in induced nitric oxide synthase, including the heart, the placenta, and the cerebral endothelium during cerebral ischemia, in the stress state, or under neurotoxicity. Overexpression of the DDAH2 gene can inhibit asymmetric dimethylarginine-induced peripheral circulating endothelial cell dysfunction. However, it is unknown whether this polymorphism regulates plasma asymmetric dimethylarginine levels in patients with leukoaraiosis. In this double-blind study, we recruited 46 patients with leukoaraiosis and 46 healthy, matched controls. Plasma asymmetric dimethylarginine levels were determined using enzyme-linked immunoassays. Genomic DNA was isolated from whole blood samples, and polymerase chain reaction, SmaI restriction enzyme digestion, restriction fragment length polymorphisms, and agarose electrophoresis were used to detect DDAH2 (-449 G/C) gene polymorphisms. The results revealed that 95.65% of leukoaraiosis patients had recessive genetic models (GG and CG), while 89.13% of healthy control subjects had dominant genetic models (CC and CG). There was a significant difference in the genotype composition ratio between leukoaraiosis patients and healthy controls (P = 0.0002). The frequency of G alleles in the leukoaraiosis patients (71.74%) was significantly higher than in healthy controls, whereas the frequency of C alleles was lower (χ2 = 13.9580, P = 0.0002). Furthermore, asymmetric dimethylarginine concentrations in subjects with the GG genotype were significantly higher than in subjects with the CG and CC genotypes (Kruskal-Wallis H = 24.5955, P < 0.0001). In addition, the GG genotype of DDAH2 (-449 G/C) was more common in patients with leukoaraiosis. These findings suggest that the G allele of DDAH2 (-449 G/C) is a risk factor for leukoaraiosis morbidity and is correlated with high levels of asymmetric dimethylarginine. This study was approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee of The 2nd Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University of China (approval No. KY2016-177) on July 28, 2016.
Keywords: allele; asymmetric dimethylarginine; cerebrovascular diseases; clinical trial; dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase 2; endothelial dysfunction; gene polymorphism; leukoaraiosis; nitric oxide.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures
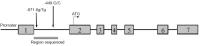
References
-
- Anavi S, Tirosh O. iNOS as a metabolic enzyme under stress conditions. Free Radic Biol Med. 2020;146:16–35. - PubMed
-
- Bode-Böger SM, Muke J, Surdacki A, Brabant G, Böger RH, Frölich JC. Oral L-arginine improves endothelial function in healthy individuals older than 70 years. Vasc Med. 2003;8:77–81. - PubMed
-
- Corsini A, Bortolini M. Drug-induced liver injury: the role of drug metabolism and transport. J Clin Pharmacol. 2013;53:463–474. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

