A difficult-to-diagnose fibromatosis-like metaplastic carcinoma of the breast: a case report
- PMID: 33433770
- PMCID: PMC7803857
- DOI: 10.1186/s40792-021-01110-0
A difficult-to-diagnose fibromatosis-like metaplastic carcinoma of the breast: a case report
Abstract
Background: Fibromatosis-like metaplastic carcinoma (FLMCa), classified as a metaplastic carcinoma of the breast, is a very rare type of metaplastic carcinoma. We report a case of FLMCa that was difficult to diagnose.
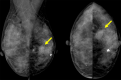
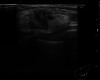
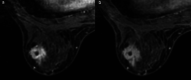
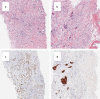
Case presentation: The patient was a 56-year-old postmenopausal woman who presented with a left-sided breast mass. A 1.3-cm irregular mass was found in the lower outer quadrant of the left breast on breast ultrasonography. She underwent core needle biopsy and vacuum-assisted biopsy, but the pathological findings only revealed inflammatory cell infiltration and a high level of fibrosis, with no malignant findings. At 3 months follow-up, she underwent a repeat breast ultrasonography, which revealed an increase in the size of the mass to 1.8 cm, and a repeat core needle biopsy, which showed a few spindle cells and squamous cells positive for cytokeratin (CK)5/6 and AE1/AE3, leading to the suspicion of FLMCa. Since the amount of tissue was insufficient to establish a definitive diagnosis, she underwent a lumpectomy. We found low-grade and slightly atypical spindle cells and partly atypical spindle cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. CK5/6 and α-SMA were positive, thus confirming FLMCa. Because the margins on the edge of the nipple side and anterior side were "ink on tumor", she underwent a mastectomy and sentinel lymph node biopsy. After the surgery, she received adjuvant chemotherapy. At 3 years and 8 months of follow-up, no recurrent or metastatic lesions were identified in her body.
Conclusions: FLMCa should be considered in the differential diagnosis when collagenous fibers are proliferating and malignancy is clinically suspected. Immunohistochemical analysis may be helpful in confirming this diagnosis.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Fibromatosis-like metaplastic carcinoma; Metaplastic carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board. WHO Classification of Tumours, 5th ed: Breast Tumours. World Health Organization; 2019, pp 134–6.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

