Multi-view classification with convolutional neural networks
- PMID: 33434208
- PMCID: PMC7802953
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0245230
Multi-view classification with convolutional neural networks
Erratum in
-
Correction: Multi-view classification with convolutional neural networks.PLoS One. 2021 Apr 8;16(4):e0250190. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0250190. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33831129 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Humans' decision making process often relies on utilizing visual information from different views or perspectives. However, in machine-learning-based image classification we typically infer an object's class from just a single image showing an object. Especially for challenging classification problems, the visual information conveyed by a single image may be insufficient for an accurate decision. We propose a classification scheme that relies on fusing visual information captured through images depicting the same object from multiple perspectives. Convolutional neural networks are used to extract and encode visual features from the multiple views and we propose strategies for fusing these information. More specifically, we investigate the following three strategies: (1) fusing convolutional feature maps at differing network depths; (2) fusion of bottleneck latent representations prior to classification; and (3) score fusion. We systematically evaluate these strategies on three datasets from different domains. Our findings emphasize the benefit of integrating information fusion into the network rather than performing it by post-processing of classification scores. Furthermore, we demonstrate through a case study that already trained networks can be easily extended by the best fusion strategy, outperforming other approaches by large margin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

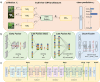

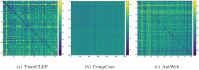
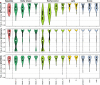
References
-
- Russakovsky O, Deng J, Su H, Krause J, Satheesh S, Ma S, et al.. ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge. International Journal of Computer Vision. 2015;115(3):211–252. 10.1007/s11263-015-0816-y - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

