Effect of intra-articular dexmedetomidine on experimental osteoarthritis in rats
- PMID: 33434210
- PMCID: PMC7802966
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0245194
Effect of intra-articular dexmedetomidine on experimental osteoarthritis in rats
Abstract
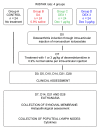
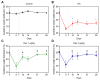
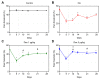
Pharmacological treatment of osteoarthritis is still inadequate due to the low efficacy of the drugs used. Dexmedetomidine via the intra-articular (i.a.) route might be an option for the treatment of osteoarthritis-associated pain. The present study assessed the analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects of dexmedetomidine administered via the i.a. route in different doses in an experimental model of rat knee osteoarthritis induced with monosodium iodoacetate. Rats were allocated to four groups with 24 animals in each group. The OA (osteoarthritis), DEX-1 (dexmedetomidine in dose of 1μg/kg) and DEX-3 (dexmedetomidine in dose of 3μg/kg) groups were subjected to induction of osteoarthritis through injection of monosodium iodoacetate (MIA) via the i.a. route on the right knee; the control group was not subjected to osteoarthritis induction. Clinical assessment was performed on day 0 (before osteoarthritis induction) and then on days 5, 10, 14, 21 and 28 after induction. Treatment was performed on day 7 via the i.a. route, consisting of dexmedetomidine in doses of 1 and 3 μg/kg, while group OA received 0.9% normal saline. The animals were euthanized on days 7, 14, 21 and 28. Samples of the synovial membrane were collected for histopathological analysis, and the popliteal lymph nodes were collected for measurement of cytokines (interleukin [IL] IL-6, tumor necrosis factor alpha [TNF-α]). Dexmedetomidine (1 and 3 μg/kg) significantly reduced the animals' weight distribution deficit during the chronic-degenerative stage of osteoarthritis and improved the pain threshold throughout the entire experiment. Histological analysis showed that dexmedetomidine did not cause any additional damage to the synovial membrane. The TNF-α levels decreased significantly in the DEX-3 group on day 28 compared with the OA group. Dexmedetomidine reduced pain, as evidenced by clinical parameters of osteoarthritis in rats, but did not have an anti-inflammatory effect on histological evaluation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Dexmedetomidine inhibits the NF-κB pathway and NLRP3 inflammasome to attenuate papain-induced osteoarthritis in rats.Pharm Biol. 2019 Dec;57(1):649-659. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2019.1651874. Pharm Biol. 2019. PMID: 31545916 Free PMC article.
-
Culture-expanded allogenic adipose tissue-derived stem cells attenuate cartilage degeneration in an experimental rat osteoarthritis model.PLoS One. 2017 Apr 18;12(4):e0176107. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0176107. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28419155 Free PMC article.
-
Osteoarthritis model induced by intra-articular monosodium iodoacetate in rats knee.Acta Cir Bras. 2016 Nov;31(11):765-773. doi: 10.1590/S0102-865020160110000010. Acta Cir Bras. 2016. PMID: 27982265
-
Resveratrol, a natural antioxidant, protects monosodium iodoacetate-induced osteoarthritic pain in rats.Biomed Pharmacother. 2016 Oct;83:763-770. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2016.06.050. Epub 2016 Jul 30. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016. PMID: 27484345
-
The role of cytokines in osteoarthritis pathophysiology.Biorheology. 2002;39(1-2):237-46. Biorheology. 2002. PMID: 12082286 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluating the effects of rifampin in the prevention of neurogenic symptoms and cardiac arrhythmias caused by the systemic toxicity of lidocaine in rats.Vet Res Forum. 2023;14(10):559-566. doi: 10.30466/vrf.2022.1985909.3724. Epub 2023 Oct 15. Vet Res Forum. 2023. PMID: 37901354 Free PMC article.
-
Dexmedetomidine Effectively Sedates Asian Elephants (Elephas maximus).Animals (Basel). 2022 Oct 15;12(20):2787. doi: 10.3390/ani12202787. Animals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36290172 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

