Digestion and Transport across the Intestinal Epithelium Affects the Allergenicity of Ara h 1 and 3 but Not of Ara h 2 and 6
- PMID: 33434390
- PMCID: PMC8047886
- DOI: 10.1002/mnfr.202000712
Digestion and Transport across the Intestinal Epithelium Affects the Allergenicity of Ara h 1 and 3 but Not of Ara h 2 and 6
Abstract
Scope: No accepted and validated methods are currently available which can accurately predict protein allergenicity. In this study, the role of digestion and transport on protein allergenicity is investigated.
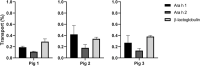
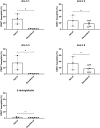
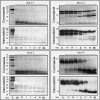
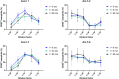
Methods and results: Peanut allergens (Ara h 1, 2, 3, and 6) and a milk allergen (β-lactoglobulin) are transported across pig intestinal epithelium using the InTESTine model and afterward basophil activation is measured to assess the (remaining) functional properties. Additionally, allergens are digested by pepsin prior to epithelial transport and their allergenicity is assessed in a human mast cell activation assay. Remarkably, transported Ara h 1 and 3 are not able to activate basophils, in contrast to Ara h 2 and 6. Digestion prior to transport results in a significant increase in mast cell activation of Ara h 1 and 3 dependent on the length of digestion time. Activation of mast cells by Ara h 2 and 6 is unaffected by digestion prior to transport.
Conclusions: Digestion and transport influences the allergenicity of Ara h 1 and 3, but not of Ara h 2 and 6. The influence of digestion and transport on protein allergenicity may explain why current in vitro assays are not predictive for allergenicity.
Keywords: allergenicity prediction; basophil and mast cell activation; food allergy; intestinal protein transport; protein digestion.
© 2021 The Authors. Molecular Nutrition & Food Research published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
2S protein Ara h 7.0201 has unique epitopes compared to other Ara h 7 isoforms and is comparable to 2S proteins Ara h 2 and 6 in basophil degranulation capacity.Clin Exp Allergy. 2018 Jul;48(7):890-897. doi: 10.1111/cea.13134. Epub 2018 Apr 11. Clin Exp Allergy. 2018. PMID: 29542223
-
Digestion of peanut allergens Ara h 1, Ara h 2, Ara h 3, and Ara h 6: a comparative in vitro study and partial characterization of digestion-resistant peptides.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2010 Dec;54(12):1711-21. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201000011. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2010. PMID: 20603832
-
Identifying Epithelial Endocytotic Mechanisms of the Peanut Allergens Ara h 1 and Ara h 2.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2017;172(2):106-115. doi: 10.1159/000451085. Epub 2017 Mar 8. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28268214
-
Proteomic screening points to the potential importance of Ara h 3 basic subunit in allergenicity of peanut.Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets. 2008 Sep;7(3):163-6. doi: 10.2174/187152808785748182. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets. 2008. PMID: 18782022 Review.
-
[Progress of researches on the allergens Ara h 1, Ara h 2 and Ara h 3 from peanut].Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2010 Dec;27(6):1401-5. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2010. PMID: 21375004 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Spatiotemporal proteolytic susceptibility of allergens: positive or negative effects on the allergic sensitization?Front Allergy. 2024 Jul 9;5:1426816. doi: 10.3389/falgy.2024.1426816. eCollection 2024. Front Allergy. 2024. PMID: 39044859 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Scientific Opinion on development needs for the allergenicity and protein safety assessment of food and feed products derived from biotechnology.EFSA J. 2022 Jan 25;20(1):e07044. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2022.7044. eCollection 2022 Jan. EFSA J. 2022. PMID: 35106091 Free PMC article.
-
Allergenic Shrimp Tropomyosin Distinguishes from a Non-Allergenic Chicken Homolog by Pronounced Intestinal Barrier Disruption and Downstream Th2 Responses in Epithelial and Dendritic Cell (Co)Culture.Nutrients. 2024 Apr 17;16(8):1192. doi: 10.3390/nu16081192. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38674882 Free PMC article.
-
An advanced in vitro human mucosal immune model to predict food sensitizing allergenicity risk: A proof of concept using ovalbumin as model allergen.Front Immunol. 2023 Jan 9;13:1073034. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1073034. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36700233 Free PMC article.
-
Immunotherapy-induced neutralizing antibodies disrupt allergen binding and sustain allergen tolerance in peanut allergy.J Clin Invest. 2023 Jan 17;133(2):e164501. doi: 10.1172/JCI164501. J Clin Invest. 2023. PMID: 36647835 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Verhoeckx K., Broekman H., Knulst A., Houben G., Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 79, 118. - PubMed
-
- Broekman H., Verhoeckx K. C., Den Hartog Jager C. F., Kruizinga A. G., Pronk‐Kleinjan M., Remington B. C., Bruijnzeel‐Koomen C. A., Houben G. F., Knulst A. C., J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 137, 1261. - PubMed
-
- Broekman H., Knulst A. C., de Jong G., Gaspari M., den Hartog Jager C. F., Houben G. F., Verhoeckx C. M., Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1601061. - PubMed
-
- EFSA Panel on Genetically Modified Organisms (GMO) , EFSA J. 2011, 9, 2150.
-
- Van Bilsen J. H. M., Sienkiewicz‐Szłapka E., Lozano‐Ojalvo D., Willemsen L. E. M., Antunes C. M., Molina E., Smit J. J., Wróblewska B., Wichers H. J., Knol E. F., Ladics G. S., Pieters R. H. H., Denery‐Papini S., Vissers Y. M., Bavaro S. L., Larré C., Verhoeckx K. C. M., Roggen E. L., Clin. Transl. Allergy 2017, 7, 13. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

