Epidemiologic Study of Cystic Fibrosis: 25 years of observational research
- PMID: 33434406
- PMCID: PMC9123916
- DOI: 10.1002/ppul.25248
Epidemiologic Study of Cystic Fibrosis: 25 years of observational research
Abstract
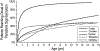
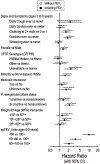
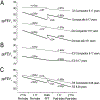
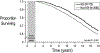
The Epidemiologic Study of Cystic Fibrosis (ESCF) was a prospective observational study of over 32,000 people with cystic fibrosis (CF) from 250 clinical care sites in North America from 1994 to 2005. Begun as a pharmacovigilance study in connection with the approval of dornase alfa in 1993, ESCF was open to all people with CF treated at any participating site in the United States or Canada. In addition to obtaining safety and effectiveness data on dornase alfa, ESCF collected encounter-based data to characterize the natural history and management of CF with a special focus on lung disease. During the study, 32,178 patients reported at least one encounter, contributing 869,136 encounters, 622,592 pulmonary function tests, 432,896 cultures, and 118,563 pulmonary exacerbations treated with intravenous antibiotics. Although ESCF data collection concluded in 2005, through a collaboration with the U.S. Cystic Fibrosis Foundation Patient Registry, additional follow-up data through 2017 was available for two-thirds of patients. This allowed for updating of CF genotype and survival information. Fifty-six peer-reviewed publications (cited over 3600 times) resulted from this study. In this manuscript we summarize the published ESCF manuscripts in thematic groups with key study findings and brief comments, and speculate on how ESCF findings will inform future data registries and patient care practices.
Keywords: cystic fibrosis; epidemiology; lung function; pulmonary exacerbation.
© 2021 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
Michael Konstan, Donald VanDevanter, Jeffrey Wagener, and Wayne Morgan have received honoraria from Genentech from serving as members of the North American Scientific Advisory Group for ESCF and have served as consultants to Genentech. Jeffrey Wagener was previously an employee of Genentech. No compensation was provided to these authors in exchange for production of this manuscript. David Pasta was previously an employee of and consultant to ICON Clinical Research, which was paid by Genentech for providing analytical services for ESCF.
Figures



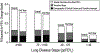
References
-
- Morgan WJ, Butler SM, Johnson CA, Colin AA, FitzSimmons SC, Geller DE, Konstan MW, Light MJ, Rabin HR, Regelmann WE, Schidlow DV, Stokes DC, Wohl ME, Kaplowitz H, Wyatt MM, Stryker S. Epidemiologic study of cystic fibrosis: design and implementation of a prospective, multicenter, observational study of patients with cystic fibrosis in the U.S. and Canada. Pediatr Pulmonol 1999;28(4):231–241. - PubMed
-
- Konstan MW, Butler SM, Schidlow DV, Morgan WJ, Julius JR, Johnson CA. Patterns of medical practice in cystic fibrosis: part I. Evaluation and monitoring of health status of patients. Investigators and Coordinators of the Epidemiologic Study of Cystic Fibrosis. Pediatr Pulmonol 1999;28(4):242–247. - PubMed
-
- Konstan MW, Butler SM, Schidlow DV, Morgan WJ, Julius JR, Johnson CA. Patterns of medical practice in cystic fibrosis: part II. Use of therapies. Investigators and Coordinators of the Epidemiologic Study of Cystic Fibrosis. Pediatr Pulmonol 1999;28(4):248–254. - PubMed
-
- Johnson CA, Butler SM, Konstan MW, Breen TJ, Morgan WJ. Estimating effectiveness in an observational study: a case study of dornase alfa in cystic fibrosis. The Investigators and Coordinators of the Epidemiologic Study of Cystic Fibrosis. J Pediatr 1999;134(6):734–739. - PubMed
-
- Geller DE, Kaplowitz H, Light MJ, Colin AA. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis in cystic fibrosis: reported prevalence, regional distribution, and patient characteristics. Scientific Advisory Group, Investigators, and Coordinators of the Epidemiologic Study of Cystic Fibrosis. Chest 1999;116(3):639–646. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

