Rheological characterization, compression, and injection molding of hydroxyapatite-silk fibroin composites
- PMID: 33434713
- PMCID: PMC7870640
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2020.120643
Rheological characterization, compression, and injection molding of hydroxyapatite-silk fibroin composites
Abstract
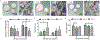
Traditional bone fixation devices made from inert metal alloys provide structural strength for bone repair but are limited in their ability to actively promote bone healing. Although several naturally derived bioactive materials have been developed to promote ossification in bone defects, it is difficult to translate small-scale benchtop fabrication of these materials to high-output manufacturing. Standard industrial molding processes, such as injection and compression molding, have typically been limited to use with synthetic polymers since most biopolymers cannot withstand the harsh processing conditions involved in these techniques. Here we demonstrate injection and compression molding of a bioceramic composite comprised of hydroxyapatite (HA) and silk fibroin (SF) from Bombyx mori silkworm cocoons. Both the molding behavior of the HA-SF slurry and final scaffold mechanics can be controlled by modulating SF protein molecular weight, SF content, and powder-to-liquid ratio. HA-SF composites with up to 20 weight percent SF were successfully molded into stable three-dimensional structures using high pressure molding techniques. The unique durability of silk fibroin enables application of common molding techniques to fabricate composite silk-ceramic scaffolds. This work demonstrates the potential to move bone tissue engineering one step closer to large-scale manufacturing of natural protein-based resorbable bone grafts and fixation devices.
Keywords: Bone grafts; Compression molding; Injection molding; Orthopedic implants; Silk-ceramic composites.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

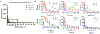
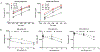

References
-
- Gardner RC, Complication of excessive compression and rigid internal fixation, J Trauma 12(6) (1972) 534–536. - PubMed
-
- Bos RRM, Boering G, Rozema FR, Leenslag JW, Resorbable poly(L-lactide) plates and screws for the fixation of zygomatic fractures, J Oral Maxillofac Surg 45(9) (1987) 751–753. - PubMed
-
- Tatum SA, Retrospective Review of Resorbable Plate Fixation in Pediatric Craniofacial Surgery Long-term Outcome, Arch Facial Plast Surg 14(1) (2012) 11–13. - PubMed
-
- Suuronen R, Kontio R, Ashammakhi N, Lindqvist C, Laine P, Bioabsorbable self-reinforced plates and screws in craniomaxillofacial surgery, Biomed Mater Eng 14(4) (2004) 517–524. - PubMed
-
- Bostman O, Pihlajamaki H, Clinical biocompatibility of biodegradable orthopaedic implants for internal fixation: a review, Biomaterials 21(24) (2000) 2615–2621. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

