Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: A Model Disease of the Past, Present and Future
- PMID: 33435150
- PMCID: PMC7827482
- DOI: 10.3390/cells10010117
Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: A Model Disease of the Past, Present and Future
Abstract
Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) has been a "model disease" with a long history. Beginning with the first discovery of leukemia and the description of the Philadelphia Chromosome and ending with the current goal of achieving treatment-free remission after targeted therapies, we describe here the journey of CML, focusing on molecular pathways relating to signaling, metabolism and the bone marrow microenvironment. We highlight current strategies for combination therapies aimed at eradicating the CML stem cell; hopefully the final destination of this long voyage.
Keywords: bone marrow microenvironment; chronic myeloid leukemia; combination therapies; history; metabolism; targeted therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
R.K. and D.S.K. hold patent no. WO2018/046666 for the use of fibronectin and integrin-linked kinase-inhibitors in leukemia.
Figures
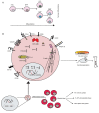
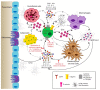

References
-
- Bennett J.H. Case of Hypertrophy of the Spleen and Liver, which Death Took Place from Suppuration of the Blood. Edinb. Med. Surg. J. 1845:413–423.
-
- Neumann E. Ein Fall von Leukämie mit Erkrankung des Knochenmarks Anhang: Salkowski: Chemische Untersuchungen des leukämischen Markes. Archiv der Heilkunde. 1871:1–15.
-
- Peter C., Nowell D.A.H. A minute chromosome in human chronic granulocytic leukemia. Science. 1960;132:1497–1499.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

