MicroRNA-Mediated Responses to Cadmium Stress in Arabidopsis thaliana
- PMID: 33435199
- PMCID: PMC7827075
- DOI: 10.3390/plants10010130
MicroRNA-Mediated Responses to Cadmium Stress in Arabidopsis thaliana
Abstract
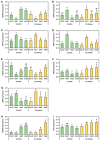
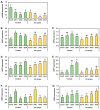
In recent decades, the presence of cadmium (Cd) in the environment has increased significantly due to anthropogenic activities. Cd is taken up from the soil by plant roots for its subsequent translocation to shoots. However, Cd is a non-essential heavy metal and is therefore toxic to plants when it over-accumulates. MicroRNA (miRNA)-directed gene expression regulation is central to the response of a plant to Cd stress. Here, we document the miRNA-directed response of wild-type Arabidopsis thaliana (Arabidopsis) plants and the drb1, drb2 and drb4 mutant lines to Cd stress. Phenotypic and physiological analyses revealed the drb1 mutant to display the highest degree of tolerance to the imposed stress while the drb2 mutant was the most sensitive. RT-qPCR-based molecular profiling of miRNA abundance and miRNA target gene expression revealed DRB1 to be the primary double-stranded RNA binding (DRB) protein required for the production of six of the seven Cd-responsive miRNAs analyzed. However, DRB2, and not DRB1, was determined to be required for miR396 production. RT-qPCR further inferred that transcript cleavage was the RNA silencing mechanism directed by each assessed miRNA to control miRNA target gene expression. Taken together, the results presented here reveal the complexity of the miRNA-directed molecular response of Arabidopsis to Cd stress.
Keywords: Arabidopsis thaliana (Arabidopsis); RT-qPCR; cadmium (Cd) stress; double-stranded RNA binding (DRB) protein; miRNA-directed gene expression regulation; microRNA (miRNA).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
DRB1, DRB2 and DRB4 Are Required for an Appropriate miRNA-Mediated Molecular Response to Osmotic Stress in Arabidopsis thaliana.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 22;25(23):12562. doi: 10.3390/ijms252312562. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684274 Free PMC article.
-
DRB1, DRB2 and DRB4 Are Required for Appropriate Regulation of the microRNA399/PHOSPHATE2 Expression Module in Arabidopsis thaliana.Plants (Basel). 2019 May 13;8(5):124. doi: 10.3390/plants8050124. Plants (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31086001 Free PMC article.
-
DRB1 and DRB2 Are Required for an Appropriate miRNA-Mediated Molecular Response to Salt Stress in Arabidopsis thaliana.Plants (Basel). 2025 Mar 15;14(6):924. doi: 10.3390/plants14060924. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40265861 Free PMC article.
-
The Arabidopsis thaliana Double-Stranded RNA Binding Proteins DRB1 and DRB2 Are Required for miR160-Mediated Responses to Exogenous Auxin.Genes (Basel). 2024 Dec 21;15(12):1648. doi: 10.3390/genes15121648. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39766914 Free PMC article.
-
DRB2 is required for microRNA biogenesis in Arabidopsis thaliana.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e35933. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0035933. Epub 2012 Apr 24. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22545148 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Miniature Inverted-Repeat Transposable Elements: Small DNA Transposons That Have Contributed to Plant MICRORNA Gene Evolution.Plants (Basel). 2023 Mar 1;12(5):1101. doi: 10.3390/plants12051101. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36903960 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Manipulation of the miR160/AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR Expression Module Impacts Root Development in Arabidopsis thaliana.Genes (Basel). 2024 Aug 7;15(8):1042. doi: 10.3390/genes15081042. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39202402 Free PMC article.
-
UVB-Pretreatment-Enhanced Cadmium Absorption and Enrichment in Poplar Plants.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 20;24(1):52. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010052. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36613496 Free PMC article.
-
Nanomaterials coupled with microRNAs for alleviating plant stress: a new opening towards sustainable agriculture.Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2022 Apr;28(4):791-818. doi: 10.1007/s12298-022-01163-x. Epub 2022 Apr 26. Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2022. PMID: 35592477 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-wide analysis of miR172-mediated response to heavy metal stress in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.): physiological, biochemical, and molecular insights.BMC Plant Biol. 2024 Nov 12;24(1):1063. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-05786-y. BMC Plant Biol. 2024. PMID: 39528933 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gayomba S.R., Jung H.-I., Yan J., Danku J., Rutzke M.A., Bernal M., Krämer U., Kochian L.V., Salt D.E., Vatamaniuk O.K. The CTR/COPT-dependent copper uptake and SPL7-dependent copper deficiency responses are required for basal cadmium tolerance in A. thaliana. Metallomics. 2013;5:1262–1275. doi: 10.1039/c3mt00111c. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

