The Protective Role of Alpha-Ketoglutaric Acid on the Growth and Bone Development of Experimentally Induced Perinatal Growth-Retarded Piglets
- PMID: 33435211
- PMCID: PMC7826854
- DOI: 10.3390/ani11010137
The Protective Role of Alpha-Ketoglutaric Acid on the Growth and Bone Development of Experimentally Induced Perinatal Growth-Retarded Piglets
Abstract
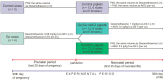
The effect of alpha-ketoglutaric acid (AKG) supplementation to experimentally-induced, perinatal growth-retarded piglets was examined. Sows were treated with a synthetic glucocorticoid (Gc) during the last 25 days of pregnancy, and after the birth, piglets were randomly divided into three groups depending on the treatment. The Gc/Gc + AKG and Gc/AKG groups born by Gc-treated sows after the birth were treated with Gc or Gc + AKG for 35 days. Significantly lower serum growth hormone, IGF-I, osteocalcin, leptin, and cortisol concentrations were observed in the Gc/Gc + AKG group, while the bone alkaline phosphatase activity was significantly higher. Serum insulin concentration was higher in the control group. Serum alanine, lysine, histidine, and tryptophan concentrations were higher in the Gc/Gc + AKG and Gc/AKG groups. The perinatal action of Gc significantly affects histomorphometry of articular cartilage and trabecular bone and bone mechanics. The results clearly showed that dietary AKG had positive effects with regards to the profile of free amino acids. Taking into account the function of AKG as an energy donor and stimulator of collagen synthesis, it can be concluded that the anabolic role of AKG may be the main mechanism responsible for its protective effect against the GC-induced perinatal intensified catabolic state.
Keywords: bone; glucocorticoid; perinatal growth-retardation; pigs; α-ketoglutaric acid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Alpha-Ketoglutarate: An Effective Feed Supplement in Improving Bone Metabolism and Muscle Quality of Laying Hens: A Preliminary Study.Animals (Basel). 2020 Dec 17;10(12):2420. doi: 10.3390/ani10122420. Animals (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33348724 Free PMC article.
-
Alpha-ketoglutarate protects the liver of piglets exposed during prenatal life to chronic excess of dexamethasone from metabolic and structural changes.J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl). 2009 Apr;93(2):192-202. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0396.2007.00805.x. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl). 2009. PMID: 19320932 Clinical Trial.
-
Dietary supplementation with glutamate precursor α-ketoglutarate attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced liver injury in young pigs.Amino Acids. 2015 Jul;47(7):1309-18. doi: 10.1007/s00726-015-1966-5. Epub 2015 Mar 21. Amino Acids. 2015. PMID: 25795418
-
Alpha-Ketoglutarate as a Molecule with Pleiotropic Activity: Well-Known and Novel Possibilities of Therapeutic Use.Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2017 Feb;65(1):21-36. doi: 10.1007/s00005-016-0406-x. Epub 2016 Jun 20. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2017. PMID: 27326424 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The biological role of a-ketoglutaric acid in physiological processes and its therapeutic potential.Dev Period Med. 2016 Jan-Mar;20(1):61-7. Dev Period Med. 2016. PMID: 27416627 Review.
Cited by
-
Essential role of the metabolite α-ketoglutarate in bone tissue and bone-related diseases.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2025 Feb 19;57(8):1207-1221. doi: 10.3724/abbs.2025020. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2025. PMID: 39967425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Analyses Provide Insights into the Growth and Development Advantages of Triploid Apostichopus japonicus.Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2022 Mar;24(1):151-162. doi: 10.1007/s10126-022-10093-4. Epub 2022 Feb 5. Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2022. PMID: 35122573 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Śliwa E., Dobrowolski P., Tatara M.R., Piersiak T., Siwicki A., Rokita E., Pierzynowski S.G. Alpha-ketoglutarate protects the liver of piglets exposed during prenatal life to chronic excess of dexamethasone from metabolic and structural changes. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2009;93:192–202. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0396.2007.00805.x. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

