Impact of Oral Targeted Therapy on the Economic Burden of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia in Canada
- PMID: 33435341
- PMCID: PMC7903280
- DOI: 10.3390/curroncol28010037
Impact of Oral Targeted Therapy on the Economic Burden of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia in Canada
Abstract
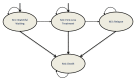
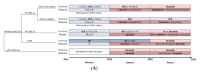
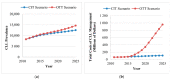
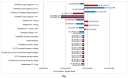
Background: Continuous oral targeted therapy (OTT) for chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) represents an effective therapy but also a major economic burden on the healthcare system. This study aimed to estimate future direct costs, along with the prevalence, of CLL in the era of continuous OTT in Canada. Methods: The economic burden of OTT was modelled and compared to chemoimmunotherapy (CIT), for CLL treatment. The burden was assessed/projected from 2011 to 2025. For the OTT scenario, CIT was considered the standard of care before 2015, while OTT was considered standard of care for patients with either unmutated immunoglobulin heavy-chain variable (IGHV) or del(17p)/TP53 mutations starting in 2015 and, from 2020 onwards, for all first-line treatments except for patients with mutated IGHV. A Markov model was developed including four health states: watchful-waiting, first-line treatment, relapse and death. Costs of therapy, follow-up/monitoring and adverse events were included. Key clinical parameters were extracted from pivotal clinical trials. Results: As incidence rates and rate of survival are increasing, the prevalence of CLL in Canada is projected to increase 1.8-fold, from 8301 patients in 2011 to 14,654 by 2025. Correspondingly, the total annual costs of CLL management are predicted to increase 15.7-fold, from $60.8 million to $957.5 million during that same period. Conclusions: Although OTT enhances survival for patients with CLL, it is nonetheless associated with an important economic burden due to the projected vast increase in costs from 2011 to 2025. Changes in clinical strategies, such as implementation of a fixed OTT treatment duration, could help alleviate financial burden.
Keywords: Markov model; chronic lymphocytic leukemia; economic burden; oral targeted therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
J.L. and C.B. are partners at PeriPharm Inc., a company that has served as a consultant to AbbVie and has received funding from AbbVie. J.L., C.B., K.G., and P.T., from PeriPharm Inc., have participated in the study conduct, data interpretation and the preparation of the manuscript. A.A. has received honoraria into a separate account within the Ottawa Hospital Research Institute, for research/academic use only. V.B. has received research funding from CIHR, Cancer Care Manitoba, Research Manitoba, Janssen and AbbVie and has served as a consultant to AbbVie, Janssen AstraZeneca, Gilead, Roche, and Lundbeck. I.F. has provided advisory consultations for AbbVie, AstraZeneca, BMS, Gilead, Janssen, Merck, Novartis, Roche and Seattle Genetics and has given presentations for AbbVie, Janssen, Novartis, Roche. C.O. has received honoraria from AbbVie, Janssen, Roche, Gilead, Merck, AstraZeneca, and Teva.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Impact of Fixed-Duration Oral Targeted Therapies on the Economic Burden of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia in Canada.Curr Oncol. 2023 Apr 24;30(5):4483-4498. doi: 10.3390/curroncol30050339. Curr Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37232797 Free PMC article.
-
Economic Burden of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia in the Era of Oral Targeted Therapies in the United States.J Clin Oncol. 2017 Jan 10;35(2):166-174. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2016.68.2856. Epub 2016 Nov 21. J Clin Oncol. 2017. PMID: 27870563 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-minimisation analysis of chronic lymphocytic leukemia in Spain in the era of oral targeted therapies.Farm Hosp. 2022 Jan 11;46(2):72-79. Farm Hosp. 2022. PMID: 35379098 English.
-
Health-related quality of life and economic burden of chronic lymphocytic leukemia in the era of novel targeted agents.Curr Med Res Opin. 2020 Sep;36(9):1481-1495. doi: 10.1080/03007995.2020.1784120. Epub 2020 Jul 23. Curr Med Res Opin. 2020. PMID: 32634056
-
Frontline Treatment for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia/Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma (CLL/SLL): Targeted Therapy vs. Chemoimmunotherapy.Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2021 Aug;16(4):325-335. doi: 10.1007/s11899-021-00637-1. Epub 2021 May 22. Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2021. PMID: 34021874 Review.
Cited by
-
Chemoimmunotherapy in the First-Line Treatment of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia: Dead Yet, or Alive and Kicking?Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jun 23;13(13):3134. doi: 10.3390/cancers13133134. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34201565 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systematic Literature Review of Economic Evaluations of Treatment Alternatives in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.BioDrugs. 2023 Mar;37(2):219-233. doi: 10.1007/s40259-023-00583-9. Epub 2023 Feb 16. BioDrugs. 2023. PMID: 36795353 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Fixed-Duration Oral Targeted Therapies on the Economic Burden of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia in Canada.Curr Oncol. 2023 Apr 24;30(5):4483-4498. doi: 10.3390/curroncol30050339. Curr Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37232797 Free PMC article.
-
The Economic Impact of Treatment Sequencing in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia in Canada Using Venetoclax plus Obinutuzumab.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Sep 17;16(18):3182. doi: 10.3390/cancers16183182. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39335154 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Bruton Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Monotherapy Compared with Combination Therapy for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia and Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Mar 27;15(7):1996. doi: 10.3390/cancers15071996. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37046657 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Leukemia and Lymphoma Society of Canada Blood Cancer in Canada-Facts and Stats. [(accessed on 16 April 2019)];2016 Available online: https://www.llscanada.org/disease-information/facts-and-statistics#Leukemia.
-
- Parikh S.A., Rabe K.G., Kay N.E., Call T.G., Ding W., Schwager S.M., Bowen D.A., Conte M., Jelinek D.F., Slager S.L., et al. Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia in Young (⩽55 years) Patients: A Comprehensive Analysis of Prognostic Factors and Outcomes. Haematologica. 2014;99:140–147. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2013.086066. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brown J., Hallek M., Pagel J. Chemoimmunotherapy Versus Targeted Treatment in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: When, How Long, How Much, and in Which Combination? ASCO Educ. Book. 2016;36:e387–e398. - PubMed
-
- Hallek M., Fischer K., Fingerle-Rowson G., Fink A.M., Busch R., Mayer J., Hensel M., Hopfinger G., Hess G., von Grünhagen U., et al. Addition of rituximab to fludarabine and cyclophosphamide in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: A randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2010;376:1164–1174. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)61381-5. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

