SAAFEC-SEQ: A Sequence-Based Method for Predicting the Effect of Single Point Mutations on Protein Thermodynamic Stability
- PMID: 33435356
- PMCID: PMC7827184
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22020606
SAAFEC-SEQ: A Sequence-Based Method for Predicting the Effect of Single Point Mutations on Protein Thermodynamic Stability
Abstract
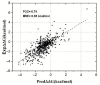
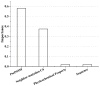
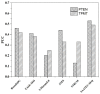
Modeling the effect of mutations on protein thermodynamics stability is useful for protein engineering and understanding molecular mechanisms of disease-causing variants. Here, we report a new development of the SAAFEC method, the SAAFEC-SEQ, which is a gradient boosting decision tree machine learning method to predict the change of the folding free energy caused by amino acid substitutions. The method does not require the 3D structure of the corresponding protein, but only its sequence and, thus, can be applied on genome-scale investigations where structural information is very sparse. SAAFEC-SEQ uses physicochemical properties, sequence features, and evolutionary information features to make the predictions. It is shown to consistently outperform all existing state-of-the-art sequence-based methods in both the Pearson correlation coefficient and root-mean-squared-error parameters as benchmarked on several independent datasets. The SAAFEC-SEQ has been implemented into a web server and is available as stand-alone code that can be downloaded and embedded into other researchers' code.
Keywords: machine learning; sequence-based; single point mutation; thermodynamics stability; web server.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SAAFEC: Predicting the Effect of Single Point Mutations on Protein Folding Free Energy Using a Knowledge-Modified MM/PBSA Approach.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Apr 7;17(4):512. doi: 10.3390/ijms17040512. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27070572 Free PMC article.
-
PROST: AlphaFold2-aware Sequence-Based Predictor to Estimate Protein Stability Changes upon Missense Mutations.J Chem Inf Model. 2022 Sep 12;62(17):4270-4282. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.2c00799. Epub 2022 Aug 16. J Chem Inf Model. 2022. PMID: 35973091
-
SAAMBE-SEQ: a sequence-based method for predicting mutation effect on protein-protein binding affinity.Bioinformatics. 2021 May 17;37(7):992-999. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btaa761. Bioinformatics. 2021. PMID: 32866236 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of protein stability upon point mutations.Biochem Soc Trans. 2007 Dec;35(Pt 6):1569-73. doi: 10.1042/BST0351569. Biochem Soc Trans. 2007. PMID: 18031268 Review.
-
Predicting the stability of mutant proteins by computational approaches: an overview.Brief Bioinform. 2021 May 20;22(3):bbaa074. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbaa074. Brief Bioinform. 2021. PMID: 32496523 Review.
Cited by
-
Opioid Addiction and Opioid Receptor Dimerization: Structural Modeling of the OPRD1 and OPRM1 Heterodimer and Its Signaling Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 24;22(19):10290. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910290. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34638633 Free PMC article.
-
Basic science methods for the characterization of variants of uncertain significance in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Aug 1;10:1238515. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1238515. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 37600050 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessing computational tools for predicting protein stability changes upon missense mutations using a new dataset.Protein Sci. 2024 Jan;33(1):e4861. doi: 10.1002/pro.4861. Protein Sci. 2024. PMID: 38084013 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of mutation-induced protein stability changes based on the geometric representations learned by a self-supervised method.BMC Bioinformatics. 2024 Aug 28;25(1):282. doi: 10.1186/s12859-024-05876-6. BMC Bioinformatics. 2024. PMID: 39198740 Free PMC article.
-
Spinocerebellar ataxia 38: structure-function analysis shows ELOVL5 G230V is proteotoxic, conformationally altered and a mutational hotspot.Hum Genet. 2023 Aug;142(8):1055-1076. doi: 10.1007/s00439-023-02572-y. Epub 2023 May 18. Hum Genet. 2023. PMID: 37199746 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ofoegbu T.C., David A., Kelley L.A., Mezulis S., Islam S.A., Mersmann S.F., Stromich L., Vakser I.A., Houlston R.S., Sternberg M.J.E. PhyreRisk: A Dynamic Web Application to Bridge Genomics, Proteomics and 3D Structural Data to Guide Interpretation of Human Genetic Variants. J. Mol. Biol. 2019;431:2460–2466. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2019.04.043. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources