Protective Effects of Polyphenol Enriched Complex Plants Extract on Metabolic Dysfunctions Associated with Obesity and Related Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Diseases in High Fat Diet-Induced C57BL/6 Mice
- PMID: 33435558
- PMCID: PMC7827276
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26020302
Protective Effects of Polyphenol Enriched Complex Plants Extract on Metabolic Dysfunctions Associated with Obesity and Related Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Diseases in High Fat Diet-Induced C57BL/6 Mice
Abstract
Background: Currently, obesity is a global health challenge due to its increasing prevalence and associated health risk. It is associated with various metabolic diseases, including diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular disease, stroke, certain forms of cancer, and non-alcoholic liver diseases (NAFLD).
Objective: The aim of this study to evaluate the effects of polyphenol enriched herbal complex (Rubus crataegifolius/ellagic acid, Crataegus pinnatifida Bunge/vitexin, chlorogenic acid, Cinnamomum cassiaa/cinnamic acid) on obesity and obesity induced NAFLD in the high-fat diet (HFD)-induced obese mouse model.
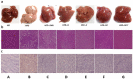
Methods: Obesity was induced in male C57BL/6 mice using HFD. After 8 weeks, the mice were treated with HFD+ plants extract for 8 weeks. Body weight, food intake weekly, and blood sugar level were measured. After sacrifice, changes in the treated group's liver weight, fat weight, serum biochemical parameters, hormone levels, and enzyme levels were measured. For histological analysis, tissues were stained with hematoxylin-eosin (H&E) and Oil Red-O.
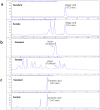
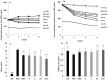
Results: Our results showed that the herbal complex ameliorated body weight and liver weight gain, and decreased total body fat in HFD-fed animals. Post prandial blood glucose (PBG) and fasting blood glucose (FBG) were lower in the herbal complex-treated group than in the HFD control group. Additionally, herbal formulation treatment significantly increased HDL levels in serum and decreased TC, TG, AST, ALT, deposition of fat droplets in the liver, and intima media thickness (IMT) in the aorta. Herbal complex increased serum adiponectin and decreased serum leptin. Herbal complex also increased carnitine palmityl transferase (CPT) activity and significantly decreased enzyme activity of beta-hydroxy beta methyl glutamyl-CoA (HMG-CoA) reductase, and fatty acid synthase (FAS).
Conclusions: The results of this study demonstrated that the herbal complex is an effective herbal formulation in the attenuation of obesity and obesity-induced metabolic dysfunction including NAFLD in HFD-induced mouse model.
Keywords: 1 Cinnamomum cassia; Crataegus pinnatifida Bunge; HFD-induced mouse model; NAFLD; Rubus crataegifolius; metabolic dysfunctions; obesity; plants extract.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no competing financial interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
An in vitro and in vivo study of a 4-herb formula on the management of diet-induced metabolic syndrome.Phytomedicine. 2018 Mar 15;42:112-125. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2018.03.028. Epub 2018 Mar 15. Phytomedicine. 2018. PMID: 29655677
-
Lycopus lucidus Turcz. ex Benth. Attenuates free fatty acid-induced steatosis in HepG2 cells and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in high-fat diet-induced obese mice.Phytomedicine. 2019 Mar 1;55:14-22. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2018.07.008. Epub 2018 Jul 18. Phytomedicine. 2019. PMID: 30668424
-
Daesiho-Tang Is an Effective Herbal Formulation in Attenuation of Obesity in Mice through Alteration of Gene Expression and Modulation of Intestinal Microbiota.PLoS One. 2016 Nov 3;11(11):e0165483. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0165483. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27812119 Free PMC article.
-
Improvements in Metabolic Health with Consumption of Ellagic Acid and Subsequent Conversion into Urolithins: Evidence and Mechanisms.Adv Nutr. 2016 Sep 15;7(5):961-72. doi: 10.3945/an.116.012575. Print 2016 Sep. Adv Nutr. 2016. PMID: 27633111 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Red Raspberries and Their Bioactive Polyphenols: Cardiometabolic and Neuronal Health Links.Adv Nutr. 2016 Jan 15;7(1):44-65. doi: 10.3945/an.115.009639. Print 2016 Jan. Adv Nutr. 2016. PMID: 26773014 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Yao-Shan of traditional Chinese medicine: an old story for metabolic health.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Aug 16;14:1194026. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1194026. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37663255 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Biological Activity Mechanism of Chlorogenic Acid and Its Applications in Food Industry: A Review.Front Nutr. 2022 Jun 29;9:943911. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.943911. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 35845802 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Ellagic Acid on Glucose and Lipid Metabolism: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Nutr Metab. 2024 Jun 17;2024:5558665. doi: 10.1155/2024/5558665. eCollection 2024. J Nutr Metab. 2024. PMID: 38915316 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatoprotective effect of lotus leaf against non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in rats via alteration of AMPK/SIRT1 and Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway.Acta Cir Bras. 2025 Aug 25;40:e407025. doi: 10.1590/acb407025. eCollection 2025. Acta Cir Bras. 2025. PMID: 40862425 Free PMC article.
-
Traditional Chinese Medicine in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: molecular insights and therapeutic perspectives.Chin Med. 2021 Aug 3;16(1):68. doi: 10.1186/s13020-021-00469-4. Chin Med. 2021. PMID: 34344394 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Moon G.S. Constituents and Uses of Medicinal Herbs. Ilweolseogak; Seoul, Korea: 1991. pp. 310–311.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

