Treatment of Brain Metastases of Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma
- PMID: 33435596
- PMCID: PMC7826874
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22020593
Treatment of Brain Metastases of Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma
Abstract
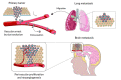
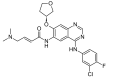
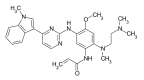
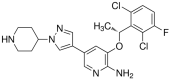
Lung cancer is one of the most common malignant neoplasms. As a result of the disease's progression, patients may develop metastases to the central nervous system. The prognosis in this location is unfavorable; untreated metastatic lesions may lead to death within one to two months. Existing therapies-neurosurgery and radiation therapy-do not improve the prognosis for every patient. The discovery of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR)-activating mutations and Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) rearrangements in patients with non-small cell lung adenocarcinoma has allowed for the introduction of small-molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitors to the treatment of advanced-stage patients. The Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) is a transmembrane protein with tyrosine kinase-dependent activity. EGFR is present in membranes of all epithelial cells. In physiological conditions, it plays an important role in the process of cell growth and proliferation. Binding the ligand to the EGFR causes its dimerization and the activation of the intracellular signaling cascade. Signal transduction involves the activation of MAPK, AKT, and JNK, resulting in DNA synthesis and cell proliferation. In cancer cells, binding the ligand to the EGFR also leads to its dimerization and transduction of the signal to the cell interior. It has been demonstrated that activating mutations in the gene for EGFR-exon19 (deletion), L858R point mutation in exon 21, and mutation in exon 20 results in cancer cell proliferation. Continuous stimulation of the receptor inhibits apoptosis, stimulates invasion, intensifies angiogenesis, and facilitates the formation of distant metastases. As a consequence, the cancer progresses. These activating gene mutations for the EGFR are present in 10-20% of lung adenocarcinomas. Approximately 3-7% of patients with lung adenocarcinoma have the echinoderm microtubule-associated protein-like 4 (EML4)/ALK fusion gene. The fusion of the two genes EML4 and ALK results in a fusion gene that activates the intracellular signaling pathway, stimulates the proliferation of tumor cells, and inhibits apoptosis. A new group of drugs-small-molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitors-has been developed; the first generation includes gefitinib and erlotinib and the ALK inhibitor crizotinib. These drugs reversibly block the EGFR by stopping the signal transmission to the cell. The second-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) afatinib or ALK inhibitor alectinib block the receptor irreversibly. Clinical trials with TKI in patients with non-small cell lung adenocarcinoma with central nervous system (CNS) metastases have shown prolonged, progression-free survival, a high percentage of objective responses, and improved quality of life. Resistance to treatment with this group of drugs emerging during TKI therapy is the basis for the detection of resistance mutations. The T790M mutation, present in exon 20 of the EGFR gene, is detected in patients treated with first- and second-generation TKI and is overcome by Osimertinib, a third-generation TKI. The I117N resistance mutation in patients with the ALK mutation treated with alectinib is overcome by ceritinib. In this way, sequential therapy ensures the continuity of treatment. In patients with CNS metastases, attempts are made to simultaneously administer radiation therapy and tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Patients with lung adenocarcinoma with CNS metastases, without activating EGFR mutation and without ALK rearrangement, benefit from immunotherapy. This therapeutic option blocks the PD-1 receptor on the surface of T or B lymphocytes or PD-L1 located on cancer cells with an applicable antibody. Based on clinical trials, pembrolizumab and all antibodies are included in the treatment of non-small cell lung carcinoma with CNS metastases.
Keywords: ALK; EGFR; brain metastases; immunotherapy; non-small cell lung carcinoma; treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Didkowska J., Wojciechowska U. Cancer in Poland in 2017. The Maria Sklodowska-Curie Memorial Cancer Center; Warsaw, Poland: 2017.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

