Behavioral factors associated with utilization of healthcare services among elderly in Pakistan: evidence from a nationally representative survey
- PMID: 33435874
- PMCID: PMC7802143
- DOI: 10.1186/s12877-021-02005-3
Behavioral factors associated with utilization of healthcare services among elderly in Pakistan: evidence from a nationally representative survey
Abstract
Background: In Pakistan, health system is facing unprecedented challenges to deal with the healthcare demand of the growing ageing population. Using conceptual framework, this study aims to analyze the factors associated with the utilization of healthcare services in private and public hospitals by the elderly population.
Methods: This study used a sample of 5319 individuals aged 60 and above extracted from the Pakistan Social and Living Standards Measurement Survey 2014-15. We followed the Anderson's Behavioral model of healthcare utilization. The behavioral factors, including predisposing, enabling and need factors, associated with the use of healthcare care were analyzed using exploratory data analysis and binary logistic regressions. The utilization of healthcare service in the study refers to the visits to private and government hospital.
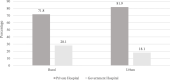
Results: Out of total 5319 participants around three-fourth or 72.4% of participants visited private hospitals for their healthcare needs. Multivariate analysis showed that older age-group (80 years and above) and participants from urban were 1.35 and 1.53 times more likely to avail healthcare service in private hospitals, respectively. The elderly persons from Khyber Pakhtunkhwa were three times (AOR: 3.29, 95%CI 2.5-4.8) more likely to visit government hospitals than their peers in Punjab. Participants who attended school (AOR: 1.21, 95%CI 0.82-1.31) were more likely to utilize healthcare service in private hospitals. Elders from rich (AOR: 1.04, 95%CI 0.84-1.13) and richest (AOR: 1.29, 95%CI 0.89-1.87) wealth quintiles were more likely to use healthcare in private hospitals. The likelihood of the utilization of healthcare service in private hospitals was 1.7 times higher for three or more consulting visits than the single visit, and 1.5 times higher in the public hospital.
Conclusions: Our findings underscore a dire need for expanding the outreach of healthcare services for the elderly population. It calls for effective implementation of policies which aim at improving equitable access to private healthcare services, and upgrading of government hospitals Moreover, the knowledge generated through this research may be employed to make social protection programs more responsive to age-related healthcare needs, and focused on caregiving for elderly living without spouse.
Keywords: Behavioral factors; Elderly health; Healthcare system; Social protection programs; Wealth quintiles.
Conflict of interest statement
The issue of the competing interests does not arise in this manuscript.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Public and private healthcare services utilization by non-institutional elderly in Hong Kong: is the inverse care law operating?Health Policy. 2009 Aug;91(3):229-38. doi: 10.1016/j.healthpol.2008.12.012. Epub 2009 Jan 22. Health Policy. 2009. PMID: 19162363
-
Determinants of healthcare utilization under the Indonesian national health insurance system - a cross-sectional study.BMC Health Serv Res. 2025 Jan 9;25(1):48. doi: 10.1186/s12913-024-11951-8. BMC Health Serv Res. 2025. PMID: 39789552 Free PMC article.
-
Factors affecting healthcare service utilization of mothers who had children with diarrhea in Ethiopia: evidence from a population based national survey.Rural Remote Health. 2015;15(4):3493. Epub 2015 Dec 24. Rural Remote Health. 2015. PMID: 26732052
-
Inequities in Antenatal Care, and Individual and Environmental Determinants of Utilization at National and Sub-national Level in Pakistan: A Multilevel Analysis.Int J Health Policy Manag. 2018 Aug 1;7(8):699-710. doi: 10.15171/ijhpm.2017.148. Int J Health Policy Manag. 2018. PMID: 30078290 Free PMC article.
-
Utilization of Sexual Reproductive Health Services Among Youths in Malaysia: A Cross-Sectional Study Applying Andersen's Behavioral Model of Healthcare Utilization.Cureus. 2024 May 13;16(5):e60230. doi: 10.7759/cureus.60230. eCollection 2024 May. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38751405 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Challenges of Elderly Caregiving in the Indian Subcontinent: A Scoping Review.Public Health Chall. 2025 Aug 18;4(3):e70085. doi: 10.1002/puh2.70085. eCollection 2025 Sep. Public Health Chall. 2025. PMID: 40831672 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Out-of-pocket expenditures associated with double disease burden in Pakistan: a quantile regression analysis.BMC Public Health. 2024 Mar 14;24(1):801. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-18320-4. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38486277 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of patient-reported outcomes in predicting 30 day all-cause readmission among older patients with heart failure.ESC Heart Fail. 2022 Oct;9(5):2840-2850. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.13991. Epub 2022 Jun 9. ESC Heart Fail. 2022. PMID: 35686326 Free PMC article.
-
Barriers to accessing eye care in Pakistan: a mixed methods study.Prim Health Care Res Dev. 2025 Jul 15;26:e58. doi: 10.1017/S1463423625100261. Prim Health Care Res Dev. 2025. PMID: 40660665 Free PMC article.
-
Improving health and social care services for slum-dwelling older adults: Perspectives of health professionals.Front Public Health. 2022 Oct 10;10:988076. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.988076. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36299759 Free PMC article.
References
-
- United Nations . World population ageing 2015. 2015.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

