COVID-19 Manifesting as Renal Allograft Dysfunction, Acute Pancreatitis, and Thrombotic Microangiopathy: A Case Report
- PMID: 33436168
- PMCID: PMC7836716
- DOI: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2020.10.048
COVID-19 Manifesting as Renal Allograft Dysfunction, Acute Pancreatitis, and Thrombotic Microangiopathy: A Case Report
Abstract
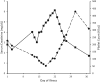
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is associated with high morbidity and mortality worldwide in both the general population and kidney transplant recipients. Acute kidney injury is a known complication of COVID-19 and appears to most commonly manifest as acute tubular injury on renal biopsy. Coagulopathy associated with COVID-19 is a known but poorly understood complication that has been reported to cause thrombotic microangiopathy on rare occasions in native kidneys of patients with COVID-19. Here, we report the first case of biopsy-proven thrombotic microangiopathy in a kidney transplant recipient with COVID-19 who developed acute pancreatitis and clinical features of microangiopathic hemolytic anemia. The patient recovered with supportive care alone.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sustained Response to Eculizumab in a Patient With COVID-19-Associated Acute Thrombotic Microangiopathy of the Allograft Kidney: A Case Report.Transplant Proc. 2023 Oct;55(8):1866-1869. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2023.03.072. Epub 2023 Apr 6. Transplant Proc. 2023. PMID: 37105825 Free PMC article.
-
Thrombotic Microangiopathy in Patients Recovering from COVID-19.MEDICC Rev. 2022 Jan 31;24(1):32-35. doi: 10.37757/MR2022.V24.N1.2. MEDICC Rev. 2022. PMID: 35157637
-
De Novo Thrombotic Microangiopathy Immediately After Kidney Transplant in Patients Without Apparent Risk Factors.Exp Clin Transplant. 2016 Apr;14(2):230-4. doi: 10.6002/ect.2014.0089. Epub 2015 May 30. Exp Clin Transplant. 2016. PMID: 26030297
-
De novo thrombotic microangiopathy following simultaneous pancreas and kidney transplantation managed with eculizumab.Nephrology (Carlton). 2017 Feb;22 Suppl 1:23-27. doi: 10.1111/nep.12936. Nephrology (Carlton). 2017. PMID: 28176480 Review.
-
De Novo and Recurrent Thrombotic Microangiopathy After Renal Transplantation: Current Concepts in Management.Exp Clin Transplant. 2022 Jun;20(6):549-557. doi: 10.6002/ect.2021.0069. Epub 2021 Sep 20. Exp Clin Transplant. 2022. PMID: 34546154 Review.
Cited by
-
Coronavirus Disease 2019-Associated Thrombotic Microangiopathy.J Hematol. 2022 Aug;11(4):148-153. doi: 10.14740/jh1019. Epub 2022 Aug 30. J Hematol. 2022. PMID: 36118551 Free PMC article.
-
Coronavirus disease 2019-associated thrombotic microangiopathy treated with plasma exchange and antihypertensive therapy in a patient with HIV: A case report with literature review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Oct 13;102(41):e35469. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000035469. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37832064 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kidney allograft biopsy findings after COVID-19.Am J Transplant. 2021 Dec;21(12):4032-4042. doi: 10.1111/ajt.16804. Epub 2021 Sep 3. Am J Transplant. 2021. PMID: 34403563 Free PMC article.
-
Necrotizing pancreatitis, microangiopathic hemolytic anemia and thrombocytopenia following the second dose of Pfizer/BioNTech COVID-19 mRNA vaccine.Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2023 Aug;135(15-16):436-440. doi: 10.1007/s00508-023-02225-0. Epub 2023 Jun 6. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2023. PMID: 37280395 Free PMC article.
-
Occam's razor or Hickam's dictum-COVID-19 is not a textbook aetiology of acute pancreatitis: A modified Naranjo Score appraisal.World J Gastroenterol. 2023 Apr 7;29(13):2050-2063. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i13.2050. World J Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 37155526 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Johns Hopkins Coronavirus Resource Center Johns Hopkins University of Medicine. https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/ [accessed 06.01.21]
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

