Importance of hyperglycemia in COVID-19 intensive-care patients: Mechanism and treatment strategy
- PMID: 33436320
- PMCID: PMC7834268
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pcd.2021.01.002
Importance of hyperglycemia in COVID-19 intensive-care patients: Mechanism and treatment strategy
Abstract
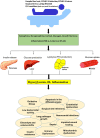
This review reported that coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infected patients with short time bed rest or quarantine and airway inflammation are at more risk of developing hyperglycemia and insulin resistance. This condition can induce oxidative stress, decrease immune system function, impair endothelial function, induce apoptosis, and reduce antioxidant in the lungs. We provide a possible mechanism in severe COVID-19 patients and recommend treatment strategy to reduce mortality rate and prevent adverse outcomes after intensive care unit (ICU).
Keywords: COVID-19; Coronavirus; Diabetes; Hyperglycemia; Oxidative stress; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2021 Primary Care Diabetes Europe. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical Study of Hyperglycemia and SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Intensive Care Unit Patients.In Vivo. 2020 Sep-Oct;34(5):3029-3032. doi: 10.21873/invivo.12136. In Vivo. 2020. PMID: 32871848 Free PMC article.
-
Managing Hyperglycemia in the COVID-19 Inflammatory Storm.Diabetes. 2020 Oct;69(10):2048-2053. doi: 10.2337/dbi20-0022. Epub 2020 Aug 10. Diabetes. 2020. PMID: 32778570
-
Outcomes in Patients With Hyperglycemia Affected by COVID-19: Can We Do More on Glycemic Control?Diabetes Care. 2020 Jul;43(7):1408-1415. doi: 10.2337/dc20-0723. Epub 2020 May 19. Diabetes Care. 2020. PMID: 32430456 Free PMC article.
-
A guidance on diagnosis and management of hyperglycemia at COVID care facilities in India.Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2021 Jan-Feb;15(1):407-413. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2021.01.015. Epub 2021 Feb 3. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2021. PMID: 33581594 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Issues for the management of people with diabetes and COVID-19 in ICU.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020 Jul 20;19(1):114. doi: 10.1186/s12933-020-01089-2. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020. PMID: 32690029 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Probiotic and resveratrol normalize GLP-1 levels and oxidative stress in the intestine of diabetic rats.Metabol Open. 2021 Apr 15;10:100093. doi: 10.1016/j.metop.2021.100093. eCollection 2021 Jun. Metabol Open. 2021. PMID: 33997755 Free PMC article.
-
The prognostic role of hyperglycemia and glucose variability in covid-related acute respiratory distress Syndrome.Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2021 May;175:108789. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2021.108789. Epub 2021 Apr 1. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2021. PMID: 33812902 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 pandemic impact on people with diabetes: results from a large representative sample of Italian older adults.Prim Care Diabetes. 2022 Oct;16(5):650-657. doi: 10.1016/j.pcd.2022.06.001. Epub 2022 Jun 20. Prim Care Diabetes. 2022. PMID: 35778238 Free PMC article.
-
Older adults' acceptance of the COVID-19 vaccine: Application of the health belief model.Nurs Open. 2023 Oct;10(10):6989-7002. doi: 10.1002/nop2.1954. Epub 2023 Jul 23. Nurs Open. 2023. PMID: 37485792 Free PMC article.
-
A Retrospective Cohort Analysis of Two Computerized Insulin Infusion Protocols.J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2023 May;17(3):635-641. doi: 10.1177/19322968231163584. Epub 2023 Mar 22. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2023. PMID: 36946553 Free PMC article.
References
-
- COVID-19 statistics, Available from: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situatio..., COVID-19 Weekly Epidemiological Update. (updated 2020; (Accessed 11 May 2020)).
-
- Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): Critical care issues. Available from: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/coronavirus-disease-2019-covid-19-crit.... (updated 2020; (Accessed 1 October 2020)).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

