Circulating long non-coding RNAs NKILA, NEAT1, MALAT1, and MIAT expression and their association in type 2 diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 33436407
- PMCID: PMC7805373
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjdrc-2020-001821
Circulating long non-coding RNAs NKILA, NEAT1, MALAT1, and MIAT expression and their association in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Circulating long non-coding RNAs NKILA, NEAT1, MALAT1, and MIAT expression and their association in type 2 diabetes mellitus.BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2025 Jan 30;13(1):e001821.ret. doi: 10.1136/bmjdrc-2020-001821.ret. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2025. PMID: 39884712 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a multifactorial disorder that leads to alterations in gene regulation. Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) have become a major research topic as they are involved in metabolic disorders.
Methods: This study included a total of 400 study subjects; 200 were subjects with T2DM and 200 were healthy subjects. Extracted RNA was used to synthesize cDNA by quantitative real time. Serum analysis was carried out to determine differences in biochemical parameters. Recorded data were used to evaluate associations with expression of lncRNAs NF-kappaB interacting lncRNA (NKILA), nuclear enriched abundant transcript 1 (NEAT1), metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1), and myocardial infarction-associated transcript (MIAT) in T2DM cases.
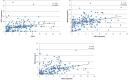
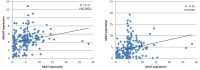
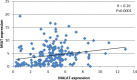
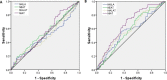
Results: Compared with healthy controls, patients with T2DM showed an overall increase in expression of lncRNAs NKILA, NEAT, MALAT1, and MIAT by 3.94-fold, 5.28-fold, 4.46-fold, and 6.35-fold, respectively. Among patients with T2DM, higher expression of lncRNA NKILA was associated with hypertension (p=0.001), smoking (p<0.0001), and alcoholism (p<0.0001). Altered NEAT1 expression was significantly associated with weight loss (p=0.04), fatigue (p=0.01), slow wound healing (p=0.002), blurred vision (p=0.008), loss of appetite (p=0.007), smoking (p<0.0001), and alcoholism (p<0.0001). Higher expression of lncRNA MALAT1 was significantly linked with weight loss (p=0.003), blurred vision (p=0.01), smoking (p<0.0001), and alcoholism (p<0.0001). Expression of lncRNA MIAT was associated with only blurred vision (p<0.0001), smoking (p<0.0001), and alcoholism (p<0.0001). Positive correlations of lncRNA NKILA with lncRNAs NEAT1 (r=0.42, p<0.0001), MALAT (r=0.36, p<0.0001) and MIAT (r=0.42, p<0.0001) were observed among patients with T2DM. Significant positive correlations of lncRNA NEAT with lncRNAs MALAT and MIAT were observed among patients with T2DM. A positive correlation between lncRNAs MALAT and MIAT was also observed among patients with T2DM.
Conclusion: Increased circulating NKILA, NEAT1, MALAT, and MIAT expression in patients with T2DM, which is linked with poor patient outcomes and significantly linked with alcoholism and smoking, may influence the degree and severity of disease among patients with T2DM. These lncRNAs may contribute to the progression of T2DM disease or other related diabetes-related complications.
Keywords: RNA; blood pressure; diabetes mellitus; gene expression; type 2.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2021. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Investigation of TNF and related lncRNAs in diabetic nephropathy.Cytokine. 2025 Apr;188:156892. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2025.156892. Epub 2025 Feb 18. Cytokine. 2025. PMID: 39970816
-
Oct4 transcriptionally regulates the expression of long non-coding RNAs NEAT1 and MALAT1 to promote lung cancer progression.Mol Cancer. 2017 Jun 14;16(1):104. doi: 10.1186/s12943-017-0674-z. Mol Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28615056 Free PMC article.
-
Linking a role of lncRNAs (long non-coding RNAs) with insulin resistance, accelerated senescence, and inflammation in patients with type 2 diabetes.Hum Genomics. 2018 Aug 23;12(1):41. doi: 10.1186/s40246-018-0173-3. Hum Genomics. 2018. PMID: 30139387 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNAs: From disease code to drug role.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021 Feb;11(2):340-354. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2020.10.001. Epub 2020 Oct 10. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021. PMID: 33643816 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long non-coding RNAs regulated NF-κB signaling in cancer metastasis: Micromanaging by not so small non-coding RNAs.Semin Cancer Biol. 2022 Oct;85:155-163. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2021.07.015. Epub 2021 Jul 24. Semin Cancer Biol. 2022. PMID: 34314819 Review.
Cited by
-
Long Noncoding RNAs in the Pathogenesis of Insulin Resistance.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 16;23(24):16054. doi: 10.3390/ijms232416054. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36555704 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting lncRNA MALAT1: A Promising Approach to Overcome Metabolic Syndrome.Int J Endocrinol. 2024 Oct 28;2024:1821252. doi: 10.1155/2024/1821252. eCollection 2024. Int J Endocrinol. 2024. PMID: 39502508 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nuclear Genome-Encoded Long Noncoding RNAs and Mitochondrial Damage in Diabetic Retinopathy.Cells. 2021 Nov 23;10(12):3271. doi: 10.3390/cells10123271. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34943778 Free PMC article.
-
Association of long non-coding RNAs NEAT1, and MALAT1 expression and pathogenesis of Behçet's disease among Egyptian patients.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2022 Aug;29(8):103344. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2022.103344. Epub 2022 Jun 16. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35800145 Free PMC article.
-
Long Non-Coding RNAs: The New Frontier into Understanding the Etiology of Alcohol Use Disorder.Noncoding RNA. 2022 Aug 4;8(4):59. doi: 10.3390/ncrna8040059. Noncoding RNA. 2022. PMID: 36005827 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
