Nanoparticle delivery of microRNA-146a regulates mechanotransduction in lung macrophages and mitigates injury during mechanical ventilation
- PMID: 33436554
- PMCID: PMC7804938
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-20449-w
Nanoparticle delivery of microRNA-146a regulates mechanotransduction in lung macrophages and mitigates injury during mechanical ventilation
Abstract
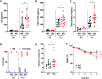
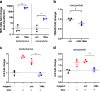
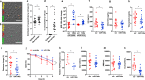
Mechanical ventilation generates injurious forces that exacerbate lung injury. These forces disrupt lung barrier integrity, trigger proinflammatory mediator release, and differentially regulate genes and non-coding oligonucleotides including microRNAs. In this study, we identify miR-146a as a mechanosensitive microRNA in alveolar macrophages that has therapeutic potential to mitigate lung injury during mechanical ventilation. We use humanized in-vitro systems, mouse models, and biospecimens from patients to elucidate the expression dynamics of miR-146a needed to decrease lung injury during mechanical ventilation. We find that the endogenous increase in miR-146a following injurious ventilation is not sufficient to prevent lung injury. However, when miR-146a is highly overexpressed using a nanoparticle delivery platform it is sufficient to prevent injury. These data indicate that the endogenous increase in microRNA-146a during mechanical ventilation is a compensatory response that partially limits injury and that nanoparticle delivery of miR-146a is an effective strategy for mitigating lung injury during mechanical ventilation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

