Carbon nano-onion-mediated dual targeting of P-selectin and P-glycoprotein to overcome cancer drug resistance
- PMID: 33436622
- PMCID: PMC7803730
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-20588-0
Carbon nano-onion-mediated dual targeting of P-selectin and P-glycoprotein to overcome cancer drug resistance
Abstract
The transmembrane P-glycoprotein (P-gp) pumps that efflux drugs are a major mechanism of cancer drug resistance. They are also important in protecting normal tissue cells from poisonous xenobiotics and endogenous metabolites. Here, we report a fucoidan-decorated silica-carbon nano-onion (FSCNO) hybrid nanoparticle that targets tumor vasculature to specifically release P-gp inhibitor and anticancer drug into tumor cells. The tumor vasculature targeting capability of the nanoparticle is demonstrated using multiple models. Moreover, we reveal the superior light absorption property of nano-onion in the near infrared region (NIR), which enables triggered drug release from the nanoparticle at a low NIR power. The released inhibitor selectively binds to P-gp pumps and disables their function, which improves the bioavailability of anticancer drug inside the cells. Furthermore, free P-gp inhibitor significantly increases the systemic toxicity of a chemotherapy drug, which can be resolved by delivering them with FSCNO nanoparticles in combination with a short low-power NIR laser irradiation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
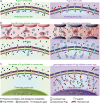
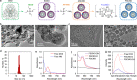
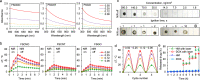
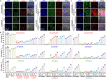


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

