Downregulation of CR6-interacting factor 1 suppresses keloid fibroblast growth via the TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway
- PMID: 33436666
- PMCID: PMC7804403
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-79785-y
Downregulation of CR6-interacting factor 1 suppresses keloid fibroblast growth via the TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway
Abstract
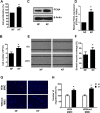
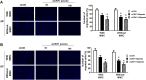
Keloids are a type of aberrant skin scarring characterized by excessive accumulation of collagen and extracellular matrix (ECM), arising from uncontrolled wound healing responses. While typically non-pathogenic, keloids are occasionally regarded as a form of benign tumor. CR6-interacting factor 1 (CRIF1) is a well-known CR6/GADD45-interacting protein, that has both nuclear and mitochondrial functions, and also exerts regulatory effects on cell growth and apoptosis. In this study, cell proliferation, cell migration, collagen production and TGF-β signaling was compared between normal fibroblasts (NFs) and keloid fibroblasts (KFs). Subsequently, the effects of CRIF1 deficiency were investigated in both NFs and KFs. Cell proliferation, cell migration, collagen production and protein expressions of TGF-β, phosphorylation of Smad2 and Smad3 were all found to be higher in KFs compared to NFs. CRIF1 deficiency in NFs and KFs inhibited cell proliferation, migration, and collagen production. In addition, phosphorylation of Smad2 and Smad3, which are transcription factors of collagen, was decreased. In contrast, mRNA expression levels of Smad7 and SMURF2, two important inhibitory proteins of Smad2/3, were increased, suggesting that CRIF1 may regulate collagen production. CRIF1 deficiency decreases the proliferation and migration of KFs, thereby inhibiting their overgrowth via the transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β)/Smad pathway. CRIF1 may therefore represent a potential therapeutic target in keloid pathogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Knockdown of FOXM1 inhibits activation of keloid fibroblasts and extracellular matrix production via inhibition of TGF-β1/Smad pathway.Life Sci. 2019 Sep 1;232:116637. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.116637. Epub 2019 Jul 6. Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 31288014
-
Knockdown of elF3a inhibits TGF‑β1‑induced extracellular matrix protein expression in keloid fibroblasts.Mol Med Rep. 2018 Mar;17(3):4057-4061. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.8365. Epub 2017 Dec 29. Mol Med Rep. 2018. PMID: 29286129
-
Silencing NLRC5 inhibits extracellular matrix expression in keloid fibroblasts via inhibition of transforming growth factor-β1/Smad signaling pathway.Biomed Pharmacother. 2016 Oct;83:1016-1021. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2016.08.012. Epub 2016 Aug 12. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016. PMID: 27525969
-
Insights into How Plant-Derived Extracts and Compounds Can Help in the Prevention and Treatment of Keloid Disease: Established and Emerging Therapeutic Targets.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 19;25(2):1235. doi: 10.3390/ijms25021235. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38279232 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Keloid disorder: Fibroblast differentiation and gene expression profile in fibrotic skin diseases.Exp Dermatol. 2021 Jan;30(1):132-145. doi: 10.1111/exd.14243. Epub 2020 Dec 20. Exp Dermatol. 2021. PMID: 33211348 Review.
Cited by
-
Keloid Disorder: Genetic Basis, Gene Expression Profiles, and Immunological Modulation of the Fibrotic Processes in the Skin.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2023 Jul 5;15(7):a041245. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a041245. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2023. PMID: 36411063 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GADD45GIP1 promotes osteosarcoma progression by modulating RPL35 ubiquitination and alleviating endoplasmic reticulum stress via the PERK/eIF2α pathway.Cancer Cell Int. 2025 Jul 2;25(1):242. doi: 10.1186/s12935-025-03866-z. Cancer Cell Int. 2025. PMID: 40604925 Free PMC article.
-
An updated review of the immunological mechanisms of keloid scars.Front Immunol. 2023 Mar 22;14:1117630. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1117630. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37033989 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deciphering Collagen Phenotype Dynamics Regulators: Insights from In-Silico Analysis.J Bioinform Syst Biol. 2024;7(3):169-181. doi: 10.26502/jbsb.5107089. Epub 2024 Sep 19. J Bioinform Syst Biol. 2024. PMID: 39484658 Free PMC article.
-
Administration of a combination of COX-2/TGF-β1 siRNAs induces hypertrophic scar fibroblast apoptosis through a TP53 mediated caspase pathway.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 2;14(1):26427. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-77756-1. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39488600 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

