The diagnostic value of human epididymis protein 4 for endometrial cancer is moderate
- PMID: 33436780
- PMCID: PMC7804086
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-79960-1
The diagnostic value of human epididymis protein 4 for endometrial cancer is moderate
Abstract
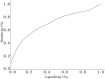
Human epididymis protein 4 (HE4) has been used as a biomarker of endometrial cancer (EC) in clinical practice. However, there remains a lack of systemic research on the critical values of HE4 for diagnosing different clinical stages and pathological types of EC. This study investigated the accuracy of human epididymis protein 4 (HE4) in the diagnosis of EC. Patients who were hospitalized for a chief complaint of abnormal vaginal hemorrhage at Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region People's Hospital between 2014 and 2019 were consecutively included. Pathological biopsy confirmed the diagnosis of EC; there were a total of 136 EC patients and 127 non-EC patients. The accuracy of HE4 in the diagnosis of EC was assessed with SPSS software. The accuracy of HE4 for diagnosing different clinical stages and pathological types of EC was also explored. The critical value of HE4 for endometrial cancer was 52.40 mmol/L, with a sensitivity of 57.35% and a specificity of 76.38%. For different stages of EC, the critical value was 36.9 mmol/L, and the sensitivity and specificity were 28% and 87.39%, respectively. For different pathological types, the critical value was 30.60 mmol/L, and the sensitivity and specificity were 93.85% and 33.33%, respectively. The diagnostic value of HE4 for EC is moderate, and the serum HE4 level cannot reflect the stage and type of EC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Siegel R, Ward E, Brawley O, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2011. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2011;61:212–236. - PubMed
-
- Amant F, Moerman P, Neven P, Timmerman D, van Limbergen E, Vergote I. Endometrial cancer. Lancet. 2005;366:491–505. - PubMed
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2013;63:11–30. - PubMed
-
- Puedie DM, Green AC. Epidemiology of endometrial cancer. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Obstet. Gynaeool. 2011;15:341–354. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials