Intermedin facilitates hepatocellular carcinoma cell survival and invasion via ERK1/2-EGR1/DDIT3 signaling cascade
- PMID: 33436794
- PMCID: PMC7803743
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-80066-x
Intermedin facilitates hepatocellular carcinoma cell survival and invasion via ERK1/2-EGR1/DDIT3 signaling cascade
Abstract
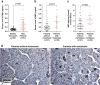
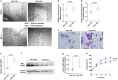
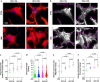
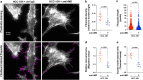
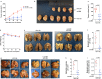
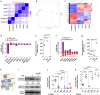
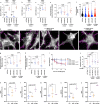
As one of the most malignant cancer types, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is highly invasive and capable of metastasizing to distant organs. Intermedin (IMD), an endogenous peptide belonging to the calcitonin family, has been suggested playing important roles in cancer cell survival and invasion, including in HCC. However, how IMD affects the behavior of HCC cells and the underlying mechanisms have not been fully elucidated. Here, we show that IMD maintains an important homeostatic state by activating the ERK1/2-EGR1 (early growth response 1) signaling cascade, through which HCC cells acquire a highly invasive ability via significantly enhanced filopodia formation. The inhibition of IMD blocks the phosphorylation of ERK1/2, resulting in EGR1 downregulation and endoplasmic reticulum stress (ER) stress, which is evidenced by the upregulation of ER stress marker DDIT3 (DNA damage-inducible transcript 3). The high level of DDIT3 induces HCC cells into an ER-stress related apoptotic pathway. Along with our previous finding that IMD plays critical roles in the vascular remodeling process that improves tumor blood perfusion, IMD may facilitate the acquisition of increased invasive abilities and a survival benefit by HCC cells, and it is easier for HCC cells to obtain blood supply via the vascular remodeling activities of IMD. According to these results, blockade of IMD activity may have therapeutic potential in the treatment of HCC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Silencing of CDCA5 inhibits cancer progression and serves as a prognostic biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma.Oncol Rep. 2018 Oct;40(4):1875-1884. doi: 10.3892/or.2018.6579. Epub 2018 Jul 17. Oncol Rep. 2018. PMID: 30015982 Free PMC article.
-
SNGH16 regulates cell autophagy to promote Sorafenib Resistance through suppressing miR-23b-3p via sponging EGR1 in hepatocellular carcinoma.Cancer Med. 2020 Jun;9(12):4324-4338. doi: 10.1002/cam4.3020. Epub 2020 Apr 23. Cancer Med. 2020. PMID: 32324343 Free PMC article.
-
lncRNA DRHC inhibits proliferation and invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma via c-Myb-regulated MEK/ERK signaling.Mol Carcinog. 2019 Mar;58(3):366-375. doi: 10.1002/mc.22934. Epub 2018 Nov 25. Mol Carcinog. 2019. PMID: 30362626
-
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 and 2 in cancer therapy: a focus on hepatocellular carcinoma.Mol Biol Rep. 2016 Feb;43(2):107-16. doi: 10.1007/s11033-016-3943-9. Epub 2016 Jan 14. Mol Biol Rep. 2016. PMID: 26767647 Review.
-
Endoplasmic reticulum stress: Multiple regulatory roles in hepatocellular carcinoma.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Oct;142:112005. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112005. Epub 2021 Aug 20. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 34426262 Review.
Cited by
-
The Expression and Function of Circadian Rhythm Genes in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 Oct 16;2021:4044606. doi: 10.1155/2021/4044606. eCollection 2021. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021. PMID: 34697563 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pdx1 Is Transcriptionally Regulated by EGR-1 during Nitric Oxide-Induced Endoderm Differentiation of Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 1;23(7):3920. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073920. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35409280 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-biological functions of intermedin in diseases.Front Physiol. 2023 Sep 6;14:1233073. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1233073. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37745233 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A multi-omics approach identifies pancreatic cancer cell extracellular vesicles as mediators of the unfolded protein response in normal pancreatic epithelial cells.J Extracell Vesicles. 2022 Jun;11(6):e12232. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12232. J Extracell Vesicles. 2022. PMID: 35656858 Free PMC article.
-
Peptidergic Systems and Cancer: Focus on Tachykinin and Calcitonin/Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide Families.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Mar 9;15(6):1694. doi: 10.3390/cancers15061694. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36980580 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

