Prediction of kinase inhibitors binding modes with machine learning and reduced descriptor sets
- PMID: 33436888
- PMCID: PMC7804204
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-80758-4
Prediction of kinase inhibitors binding modes with machine learning and reduced descriptor sets
Abstract
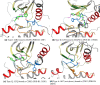
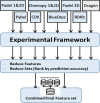
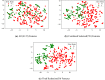
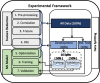
Protein kinases are receiving wide research interest, from drug perspective, due to their important roles in human body. Available kinase-inhibitor data, including crystallized structures, revealed many details about the mechanism of inhibition and binding modes. The understanding and analysis of these binding modes are expected to support the discovery of kinase-targeting drugs. The huge amounts of data made it possible to utilize computational techniques, including machine learning, to help in the discovery of kinase-targeting drugs. Machine learning gave reasonable predictions when applied to differentiate between the binding modes of kinase inhibitors, promoting a wider application in that domain. In this study, we applied machine learning supported by feature selection techniques to classify kinase inhibitors according to their binding modes. We represented inhibitors as a large number of molecular descriptors, as features, and systematically reduced these features in a multi-step manner while trying to attain high classification accuracy. Our predictive models could satisfy both goals by achieving high accuracy while utilizing at most 5% of the modeling features. The models could differentiate between binding mode types with MCC values between 0.67 and 0.92, and balanced accuracy values between 0.78 and 0.97 for independent test sets.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Machine Learning Models for Accurate Prediction of Kinase Inhibitors with Different Binding Modes.J Med Chem. 2020 Aug 27;63(16):8738-8748. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.9b00867. Epub 2019 Aug 30. J Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 31469557
-
Benchmarking Cross-Docking Strategies in Kinase Drug Discovery.J Chem Inf Model. 2024 Dec 9;64(23):8848-8858. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.4c00905. Epub 2024 Nov 18. J Chem Inf Model. 2024. PMID: 39558632 Free PMC article.
-
Binding Activity Prediction of Cyclin-Dependent Inhibitors.J Chem Inf Model. 2015 Jul 27;55(7):1469-82. doi: 10.1021/ci500633c. Epub 2015 Jul 10. J Chem Inf Model. 2015. PMID: 26079845
-
Unexpected off-targets and paradoxical pathway activation by kinase inhibitors.ACS Chem Biol. 2015 Jan 16;10(1):234-45. doi: 10.1021/cb500886n. Epub 2015 Jan 2. ACS Chem Biol. 2015. PMID: 25531586 Review.
-
Perspective on computational and structural aspects of kinase discovery from IPK2014.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Oct;1854(10 Pt B):1595-604. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2015.03.014. Epub 2015 Apr 7. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25861861 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Zebrafish as model system for the biological characterization of CK1 inhibitors.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Sep 11;14:1245246. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1245246. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37753113 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive exploration of the druggable conformational space of protein kinases using AI-predicted structures.PLoS Comput Biol. 2024 Jul 24;20(7):e1012302. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1012302. eCollection 2024 Jul. PLoS Comput Biol. 2024. PMID: 39046952 Free PMC article.
-
Interpretable Machine Learning Models for Molecular Design of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Using Variational Autoencoders and Perturbation-Based Approach of Chemical Space Exploration.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 24;23(19):11262. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911262. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36232566 Free PMC article.
-
Large-scale comparison of machine learning methods for profiling prediction of kinase inhibitors.J Cheminform. 2024 Jan 30;16(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s13321-023-00799-5. J Cheminform. 2024. PMID: 38291477 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacology activity, toxicity, and clinical trials of Erythrina genus plants (Fabaceae): an evidence-based review.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Nov 16;14:1281150. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1281150. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 38044940 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abdelbaky IZ, Al-Sadek AF, Badr AA. Applying machine learning techniques for classifying cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2018;9:229–235.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

