Effectiveness of a toothpaste and a serum containing calcium silicate on protecting the enamel after interproximal reduction against demineralization
- PMID: 33437013
- PMCID: PMC7804454
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-80844-7
Effectiveness of a toothpaste and a serum containing calcium silicate on protecting the enamel after interproximal reduction against demineralization
Abstract
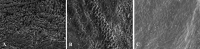
To evaluate the effectiveness of a calcium silicate/phosphate fluoridated tooth paste and a serum compared with a toothpaste containing hydroxyapatite on protecting the enamel after interproximal reduction against demineralization. 3 sets of eleven incisors were created. The teeth underwent interproximal enamel reduction (IER) of 0.5 mm. Each set was allocated to one of three groups: (1) Brushing without toothpaste (control group); (2) Vitis toothpaste + Remin Pro; (3) Regenerate toothpaste + Regenerate Serum. The agents were applied three times a day and specimens subjected to demineralization cycles for 30 days. The weight percentages of calcium (Ca) and phosphorous (P) were quantified by X-ray microfluorescence spectroscopy. Surface microhardness measurements and electron scanning microscopy (SEM) observations were made. Ca data and the Ca/P ratio were significantly higher in Group 3 than the other groups (p < 0.017), while P was significantly lower in Group 3 (p < 0.017). No significant differences were found between Groups 1 and 2 (p > 0.017). Group 3 showed significantly higher microhardness values (p < 0.05) than Group 1. No significant differences were found for other comparisons between groups (p < 0.05). SEM images showed less demineralization in Group 3. The application of a calcium silicate/phosphate fluoridated tooth paste (Regenerate advance) and a dual serum (Regenerate advance enamel serum) protect the enamel with interproximal reduction against demineralization. Therefore, this treatment could be used to prevent the dissolution of hydroxyapatite after IER.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Remineralisation effect of a dual-phase calcium silicate/phosphate gel combined with calcium silicate/phosphate toothpaste on acid-challenged enamel in situ.J Dent. 2014 Jun;42 Suppl 1:S53-9. doi: 10.1016/S0300-5712(14)50008-5. J Dent. 2014. PMID: 24993856 Clinical Trial.
-
Introduction of an interproximal mineralisation model to measure remineralisation caused by novel formulations containing calcium silicate, sodium phosphate salts and fluoride.J Dent. 2014 Jun;42 Suppl 1:S46-52. doi: 10.1016/S0300-5712(14)50007-3. J Dent. 2014. PMID: 24993855
-
Enhanced enamel benefits from a novel toothpaste and dual phase gel containing calcium silicate and sodium phosphate salts.J Dent. 2014 Jun;42 Suppl 1:S39-45. doi: 10.1016/S0300-5712(14)50006-1. J Dent. 2014. PMID: 24993854
-
Remineralization efficacy of a toothpaste containing 8% arginine and calcium carbonate on enamel surface.Am J Dent. 2013 Oct;26(5):291-7. Am J Dent. 2013. PMID: 24479283
-
Demineralization-remineralization dynamics in teeth and bone.Int J Nanomedicine. 2016 Sep 19;11:4743-4763. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S107624. eCollection 2016. Int J Nanomedicine. 2016. PMID: 27695330 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Enamel Remineralization Efficacy of Coconut Milk and Lyophilized Coconut Extract in Different Concentrations on Demineralized Enamel Surfaces: An In-Vitro Study.Cureus. 2023 Sep 5;15(9):e44712. doi: 10.7759/cureus.44712. eCollection 2023 Sep. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37809240 Free PMC article.
-
An In-Vitro Comparative Study of Fluoride Varnish and Two Calcium-Containing Fluoride Products on the Remineralization of Primary Teeth Enamel.Front Dent. 2023 Jul 8;20:23. doi: 10.18502/fid.v20i23.13167. eCollection 2023. Front Dent. 2023. PMID: 37701656 Free PMC article.
-
New Generation of Orthodontic Elastomeric Ligature to Prevent Enamel Demineralization In Vivo.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 1;25(15):8409. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158409. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39125977 Free PMC article.
-
The use of hydroxyapatite toothpaste to prevent dental caries.Odontology. 2022 Apr;110(2):223-230. doi: 10.1007/s10266-021-00675-4. Epub 2021 Nov 22. Odontology. 2022. PMID: 34807345 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of Resin Infiltration, Fluoride and the Biomimetic Mineralization of CPP-ACP in Protecting Enamel after Orthodontic Inter-Proximal Enamel Reduction.Biomimetics (Basel). 2023 Feb 14;8(1):82. doi: 10.3390/biomimetics8010082. Biomimetics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36810413 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barbero JG. Patología y terapeútica dental. García Barbero J. Síntesis. Madrid. 2000;32:468–482.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous