Role of ultrasonographic inferior venacaval assessment in averting spinal anaesthesia-induced hypotension for hernia and hydrocele surgeries-A prospective randomised controlled study
- PMID: 33437072
- PMCID: PMC7791418
- DOI: 10.4103/ija.IJA_244_20
Role of ultrasonographic inferior venacaval assessment in averting spinal anaesthesia-induced hypotension for hernia and hydrocele surgeries-A prospective randomised controlled study
Abstract
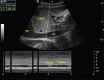
Background and aims: Hypotension is one of the most common side effects of spinal anaesthesia and preoperative volume status is one of the predictive variables for developing spinal-induced hypotension (SIH). Inferior venacaval ultrasound (IVCUS) is effective to assess fluid responsiveness in critical care patients. The aim of this study was to evaluate the IVCUS-guided volume optimisation prior to spinal anaesthesia to prevent SIH and requirement of vasopressors.
Methods: Eighty patients undergoing inguinal hernia/hydrocele surgeries under spinal anaesthesia were randomised into group A consisting of an IVCUS-guided volume optimisation before spinal anaesthesia and group B with no IVCUS assessment. Unpaired t-test and Z test were used for statistical analysis. Pearson's correlation coefficient was used to find correlation. The primary outcome was relative risk reduction in the incidence of SIH between the groups. Secondary outcomes were the need for vasopressor drugs, the total volume of fluids required throughout procedure, and correlation between IVC collapsibility index (IVCCI) versus prespinal fluids, IVCCI versus baseline mean arterial pressure (MAP).
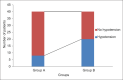
Results: The relative risk reduction in the incidence of SIH was lower in group A compared to group B which was 40% (P = 0.002 CI = 95%). The SIH in group A was 20% and group B was 50%. There was decreased requirement of vasopressors in group A compared to group B. Total IV fluids given was more in group A. There was a positive correlation between IVCCI and pre-spinal fluids.
Conclusion: IVCUS assessment reduces the SIH as well as requirement of vasopressor for hernia and hydrocele surgeries.
Keywords: Hypotension; IVC collapsibility index; IVC ultrasound; spinal anaesthesia.
Copyright: © 2020 Indian Journal of Anaesthesia.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Hartmann B, Junger A, Klasen J, Benson M, Jost A, Banzhaf A, et al. The incidence and risk factors for hypotension after spinal anesthesia induction: An analysis with automated data collection. Anesth Analg. 2002;94:1521–9. - PubMed
-
- Zhang J, Critchley LA. Inferior vena cava ultrasonography before general anesthesia can predict hypotension after induction. Anesthesiology. 2016;124:580–9. - PubMed
-
- Carpenter RL, Caplan RA, Brown DL, Stephenson C, Wu R. Incidence and risk factors for side effects of spinal anesthesia. Anesthesiology. 1992;76:906–16. - PubMed
-
- Singh J, Ranjit S, Shrestha S, Sharma R, Marahatta SB. Effect of preloading on hemodynamic of the patient undergoing surgery under spinal anaesthesia. Kathmandu Univ Med J. 2010;8:216–21. - PubMed
-
- Khan MU, Memon AS, Ishaq M, Aqil M. Preload versus coload and vasopressor requirement for the prevention of spinal anesthesia induced hypotension in nonobstetric patients. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2015;25:851–5. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
