Phytochemical analysis of Panax species: a review
- PMID: 33437152
- PMCID: PMC7790905
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jgr.2019.12.009
Phytochemical analysis of Panax species: a review
Abstract
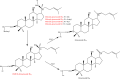
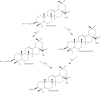
Panax species have gained numerous attentions because of their various biological effects on cardiovascular, kidney, reproductive diseases known for a long time. Recently, advanced analytical methods including thin layer chromatography, high-performance thin layer chromatography, gas chromatography, high-performance liquid chromatography, ultra-high performance liquid chromatography with tandem ultraviolet, diode array detector, evaporative light scattering detector, and mass detector, two-dimensional high-performance liquid chromatography, high speed counter-current chromatography, high speed centrifugal partition chromatography, micellar electrokinetic chromatography, high-performance anion-exchange chromatography, ambient ionization mass spectrometry, molecularly imprinted polymer, enzyme immunoassay, 1H-NMR, and infrared spectroscopy have been used to identify and evaluate chemical constituents in Panax species. Moreover, Soxhlet extraction, heat reflux extraction, ultrasonic extraction, solid phase extraction, microwave-assisted extraction, pressurized liquid extraction, enzyme-assisted extraction, acceleration solvent extraction, matrix solid phase dispersion extraction, and pulsed electric field are discussed. In this review, a total of 219 articles published from 1980 to 2018 are investigated. Panax species including P. notoginseng, P. quinquefolius, sand P. ginseng in the raw and processed forms from different parts, geographical origins, and growing times are studied. Furthermore, the potential biomarkers are screened through the previous articles. It is expected that the review can provide a fundamental for further studies.
Keywords: Analytical methods; Application; Content; Panax species; Sample preparations.
© 2020 The Korean Society of Ginseng. Publishing services by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
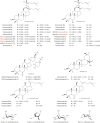
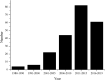
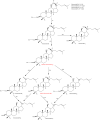
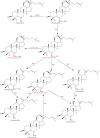
References
-
- Lu Q. A review on studies of Panax plant taxonomy. J Jilin Agr Univ. 1992;14:107–111.
-
- The State Pharmacopoeia Commission . 2015. Chinese Pharmacopoeia. Beijing.
-
- Ru W., Wang D., Xu Y., He X., Sun Y.E., Qian L., Zhou X., Qin Y. Chemical constituents and bioactivities of Panax ginseng (C. A. Mey.) Drug Discov Ther. 2015;9:23–32. - PubMed
-
- Yang W.Z., Hu Y., Wu W.Y., Ye M., Guo D.A. Saponins in the genus Panax L. (Araliaceae): a systematic review of their chemical diversity. Phytochemistry. 2014;106:7–24. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

