Glycosyltransformation of ginsenoside Rh2 into two novel ginsenosides using recombinant glycosyltransferase from Lactobacillus rhamnosus and its in vitro applications
- PMID: 33437156
- PMCID: PMC7790896
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jgr.2019.11.004
Glycosyltransformation of ginsenoside Rh2 into two novel ginsenosides using recombinant glycosyltransferase from Lactobacillus rhamnosus and its in vitro applications
Abstract
Background: Ginsenoside Rh2 is well known for many pharmacological activities, such as anticancer, antidiabetes, antiinflammatory, and antiobesity properties. Glycosyltransferases (GTs) are ubiquitous enzymes present in nature and are widely used for the synthesis of oligosaccharides, polysaccharides, glycoconjugates, and novel derivatives. We aimed to synthesize new ginsenosides from Rh2 using the recombinant GT enzyme and investigate its cytotoxicity with diverse cell lines.
Methods: We have used a GT gene with 1,224-bp gene sequence cloned from Lactobacillus rhamnosus (LRGT) and then expressed in Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3). The recombinant GT protein was purified and demonstrated to transform Rh2 into two novel ginsenosides, and they were characterized by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) techniques and evaluated by 3-(4, 5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2-5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay.
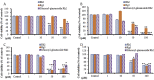
Results: Two novel ginsenosides with an additional glucopyranosyl (6→1) and two additional glucopyranosyl (6→1) linked with the C-3 position of the substrate Rh2 were synthesized, respectively. Cell viability assay in the lung cancer (A549) cell line showed that glucosyl ginsenoside Rh2 inhibited cell viability more potently than ginsenoside Rg3 and Rh2 at a concentration of 10 μM. Furthermore, glucosyl ginsenoside Rh2 did not exhibit any cytotoxic effect in murine macrophage cells (RAW264.7), mouse embryo fibroblasts cells (3T3-L1), and skin cells (B16BL6) at a concentration of 10 μM compared with ginsenoside Rh2 and Rg3.
Conclusion: This is the first report on the synthesis of two novel ginsenosides, namely, glucosyl ginsenoside Rh2 and diglucosyl ginsenoside Rh2 from Rh2 by using recombinant GT isolated from L. rhamnosus. Moreover, diglucosyl ginsenoside Rh2 might be a new candidate for treatment of inflammation, obesity, and skin whiting, and especially for anticancer.
Keywords: Cell viability; Ginsenoside Rh2; Glycosyltransferase; Novel ginsenosides.
© 2020 The Korean Society of Ginseng. Publishing services by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to report.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Comparative analysis of the expression level of recombinant ginsenoside-transforming β-glucosidase in GRAS hosts and mass production of the ginsenoside Rh2-Mix.PLoS One. 2017 Apr 19;12(4):e0176098. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0176098. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28423055 Free PMC article.
-
Cloning and heterologous expression of UDP-glycosyltransferase genes from Bacillus subtilis and its application in the glycosylation of ginsenoside Rh1.Lett Appl Microbiol. 2015 Jan;60(1):72-8. doi: 10.1111/lam.12339. Epub 2014 Nov 16. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25327709
-
Enhanced production of ginsenoside Rh2(S) from PPD-type major ginsenosides using BglSk cloned from Saccharibacillus kuerlensis together with two glycosidase in series.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2021 Aug;28(8):4668-4676. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.04.079. Epub 2021 May 1. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34354454 Free PMC article.
-
Anticancer property of ginsenoside Rh2 from ginseng.Eur J Med Chem. 2020 Oct 1;203:112627. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112627. Epub 2020 Jul 13. Eur J Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32702586 Review.
-
Potential of ginsenoside Rh2and its derivatives as anti-cancer agents.Chin J Nat Med. 2022 Dec;20(12):881-901. doi: 10.1016/S1875-5364(22)60193-6. Chin J Nat Med. 2022. PMID: 36549803 Review.
Cited by
-
The ways for ginsenoside Rh2 to fight against cancer: the molecular evidences in vitro and in vivo.J Ginseng Res. 2023 Mar;47(2):173-182. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2022.09.011. Epub 2022 Oct 6. J Ginseng Res. 2023. PMID: 36926617 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of Emerging Techniques in Reduction of the Sugar Content of Fruit Juice: Current Challenges and Future Perspectives.Foods. 2023 Mar 10;12(6):1181. doi: 10.3390/foods12061181. Foods. 2023. PMID: 36981108 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ginsenoside Rh2 suppresses ferroptosis in ulcerative colitis by targeting specific protein 1 by upregulating microRNA-125a-5p.Eur J Med Res. 2024 Sep 2;29(1):450. doi: 10.1186/s40001-024-02025-w. Eur J Med Res. 2024. PMID: 39223620 Free PMC article.
-
Progress on the Elucidation of the Antinociceptive Effect of Ginseng and Ginsenosides in Chronic Pain.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Feb 21;13:821940. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.821940. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35264958 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biosynthesis of a Novel Ginsenoside with High Anticancer Activity by Recombinant UDP-Glycosyltransferase and Characterization of Its Biological Properties.Molecules. 2025 Feb 14;30(4):898. doi: 10.3390/molecules30040898. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40005208 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Radad K., Gille G., Liu L., Rausch W.D. Use of ginseng in medicine with emphasis on neurodegenerative disorders. J Pharmacol Sci. 2006;100:175–186. - PubMed
-
- Park E.J., Yi J., Chung K.H., Ryu D.Y., Choi J., Park K. Oxidative stress and apoptosis induced by titanium dioxide nanoparticles in cultured BEAS-2B cells. Toxicol Lett. 2008;180:222–229. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

