Clemastine promotes recovery of neural function and suppresses neuronal apoptosis by restoring balance of pro-inflammatory mediators in an experimental model of intracerebral hemorrhage
- PMID: 33437198
- PMCID: PMC7797547
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.51150
Clemastine promotes recovery of neural function and suppresses neuronal apoptosis by restoring balance of pro-inflammatory mediators in an experimental model of intracerebral hemorrhage
Abstract
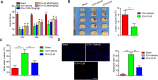
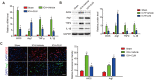
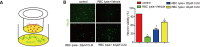
Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) represents a common acute cerebrovascular event that imparts high rates of disability. The microglia-mediated inflammatory response is a critical factor in determining cerebral damage post-ICH. Clemastine (CLM) is a histamine receptor H1 (HRH1) antagonist that has been shown to modulate the inflammatory response. However, the effects of CLM on ICH and the underlying mechanism remain to be determined. This investigation reveals that CLM resulted in reduction of cerebral hematoma volume, decreased cerebral edema and lower rates of neuronal apoptosis as well as improved behavioral scores in an acute ICH murine model. CLM treatment was noted to decrease pro-inflammatory effectors and increased anti-inflammatory effectors post-ICH. In addition, CLM reduced the deleterious effects of activated microglia on neurons in a transwell co-culture system. Our findings show that CLM likely mediates its therapeutic effect through inhibition of microglia-induced inflammatory response and apoptosis, thereby enhancing restoration of neuronal function.
Keywords: Clemastine; Intracerebral hemorrhage; histamine receptor H1.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Raddeanin A (RA) reduced acute inflammatory injury in mouse experimental cerebral hemorrhage by suppression of TLR4.Int J Med Sci. 2022 Jul 11;19(8):1235-1240. doi: 10.7150/ijms.73007. eCollection 2022. Int J Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 35928716 Free PMC article.
-
Proteasomal inhibition in intracerebral hemorrhage: neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory effects of bortezomib.Neurosci Res. 2007 May;58(1):12-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neures.2007.01.006. Epub 2007 Jan 19. Neurosci Res. 2007. PMID: 17328981
-
Gastrodin Attenuates Neuronal Apoptosis and Neurological Deficits after Experimental Intracerebral Hemorrhage.J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2020 Jan;29(1):104483. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2019.104483. Epub 2019 Nov 11. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2020. PMID: 31727597
-
Neuroprotective Therapies for Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage.Neurocrit Care. 2021 Dec;35(3):862-886. doi: 10.1007/s12028-021-01311-3. Epub 2021 Aug 2. Neurocrit Care. 2021. PMID: 34341912 Review.
-
Advances in neuroprotective strategies: potential therapies for intracerebral hemorrhage.Cerebrovasc Dis. 2011;31(3):211-22. doi: 10.1159/000321870. Epub 2010 Dec 21. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2011. PMID: 21178344 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neuroprotective Effect of Clemastine Improved Oligodendrocyte Proliferation through the MAPK/ERK Pathway in a Neonatal Hypoxia Ischemia Rat Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 27;25(15):8204. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158204. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39125778 Free PMC article.
-
Insights on therapeutic potential of clemastine in neurological disorders.Front Mol Neurosci. 2023 Sep 28;16:1279985. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2023.1279985. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37840769 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Positive effect of evobrutinib in CNS remyelination models and lack of synergy with clemastine-A dose response study.Mult Scler J Exp Transl Clin. 2025 Mar 21;11(1):20552173251326913. doi: 10.1177/20552173251326913. eCollection 2025 Jan-Mar. Mult Scler J Exp Transl Clin. 2025. PMID: 40125491 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing the efficacy in reducing brain injury of different neuroprotective agents following neonatal hypoxia-ischemia in newborn rats: a multi-drug randomized controlled screening trial.Sci Rep. 2023 Jun 10;13(1):9467. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-36653-9. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37301929 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging therapeutic application of clemastine: a review of recent patents updates.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Aug;398(8):9609-9622. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-03978-3. Epub 2025 Mar 7. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40055203 Review.
References
-
- Cordonnier C, Demchuk A, Ziai W, Anderson C. Intracerebral haemorrhage: Current approaches to acute management. Lancet (London, England) 2018;392:1257–1268. - PubMed
-
- Burns J, Fisher J, Cervantes-Arslanian A. Recent advances in the acute management of intracerebral hemorrhage. Neurosurgery clinics of North America. 2018;29:263–272. - PubMed
-
- Haller J, Wiss A, May C, Jones G, Smetana K. Acute management of hypertension following intracerebral hemorrhage. Critical care nursing quarterly. 2019;42:129–147. - PubMed
-
- Liao K, Sung C, Huang Y, Li W, Yu P, Wang J. Therapeutic potential of drugs targeting pathophysiology of intracerebral hemorrhage: From animal models to clinical applications. Current pharmaceutical design. 2017;23:2212–2225. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

