P - cresol and Indoxyl Sulfate Impair Osteogenic Differentiation by Triggering Mesenchymal Stem Cell Senescence
- PMID: 33437209
- PMCID: PMC7797544
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.48492
P - cresol and Indoxyl Sulfate Impair Osteogenic Differentiation by Triggering Mesenchymal Stem Cell Senescence
Abstract
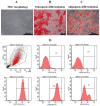
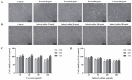
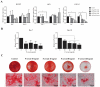
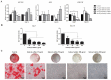
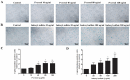
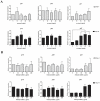
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients obtained high levels of uremic toxins progressively develop several complications including bone fractures. Protein-bound uremic toxins especially p-cresol and indoxyl sulfate are hardly eliminated due to their high molecular weight. Thus, the abnormality of bone in CKD patient could be potentially resulted from the accumulation of uremic toxins. To determine whether protein-bound uremic toxins have an impact on osteogenesis, mesenchymal stem cells were treated with either p-cresol or indoxyl sulfate under in vitro osteogenic differentiation. The effects of uremic toxins on MSC-osteoblastic differentiation were investigated by evaluation of bone phenotype. The results demonstrated that p-cresol and indoxyl sulfate down-regulated the transcriptional level of collagen type I, deceased alkaline phosphatase activity, and impaired mineralization of MSC-osteoblastic cells. Furthermore, p-cresol and indoxyl sulfate gradually increased senescence-associated beta-galactosidase positive cells while upregulated the expression of p21 which participate in senescent process. Our findings clearly revealed that the presence of uremic toxins dose-dependently influenced a gradual deterioration of osteogenesis. The effects partially mediate through the activation of senescence-associated gene lead to the impairment of osteogenesis. Therefore, the management of cellular senescence triggered by uremic toxins could be considered as an alternative therapeutic approach to prevent bone abnormality in CKD patients.
Keywords: cellular senescence; chronic kidney disease; indoxyl sulfate; mesenchymal stem cells; osteogenesis; p-cresol.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impacts of Indoxyl Sulfate and p-Cresol Sulfate on Chronic Kidney Disease and Mitigating Effects of AST-120.Toxins (Basel). 2018 Sep 11;10(9):367. doi: 10.3390/toxins10090367. Toxins (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30208594 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein-bound uremic toxins: new culprits of cardiovascular events in chronic kidney disease patients.Toxins (Basel). 2014 Feb 20;6(2):665-78. doi: 10.3390/toxins6020665. Toxins (Basel). 2014. PMID: 24561478 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein-Bound Uremic Toxins and Immunity.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2325:215-227. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1507-2_15. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 34053061 Review.
-
Uremic toxins impair human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells functionality in vitro.Exp Toxicol Pathol. 2014 Jul;66(4):187-94. doi: 10.1016/j.etp.2014.01.003. Epub 2014 Feb 16. Exp Toxicol Pathol. 2014. PMID: 24548687
-
SLC22A11 Inserts the Uremic Toxins Indoxyl Sulfate and P-Cresol Sulfate into the Plasma Membrane.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 14;24(20):15187. doi: 10.3390/ijms242015187. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37894870 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The uremic toxin indoxyl sulfate decreases osteocyte RANKL/OPG and increases Wnt inhibitor RNA expression that is reversed by PTH.JBMR Plus. 2024 Oct 29;9(1):ziae136. doi: 10.1093/jbmrpl/ziae136. eCollection 2025 Jan. JBMR Plus. 2024. PMID: 39664935 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic Kidney Disease and Osteoarthritis: Current Understanding and Future Research Directions.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 13;26(4):1567. doi: 10.3390/ijms26041567. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40004032 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interplay between gut microbiota, bone health and vascular calcification in chronic kidney disease.Eur J Clin Invest. 2021 Sep;51(9):e13588. doi: 10.1111/eci.13588. Epub 2021 Jun 7. Eur J Clin Invest. 2021. PMID: 33948936 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Applications of Metabolomics in Calcium Metabolism Disorders in Humans.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 8;23(18):10407. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810407. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142318 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of p-cresol, a uremic toxin, on cancer cells.Transl Cancer Res. 2023 Feb 28;12(2):367-374. doi: 10.21037/tcr-22-2042. Epub 2023 Jan 5. Transl Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 36915599 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Webster AC, Nagler EV, Morton RL, Masson P. Chronic Kidney Disease. Lancet (London, England) 2017;389:1238–52. - PubMed
-
- Gao H, Liu S. Role of uremic toxin indoxyl sulfate in the progression of cardiovascular disease. Life sciences. 2017;185:23–9. - PubMed
-
- Nangaku M, Mimura I, Yamaguchi J, Higashijima Y, Wada T, Tanaka T. Role of uremic toxins in erythropoiesis-stimulating agent resistance in chronic kidney disease and dialysis patients. Journal of renal nutrition: the official journal of the Council on Renal Nutrition of the National Kidney Foundation. 2015;25:160–3. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

