Acute Bilateral Uveitis, Hypotony, and Cataracts Associated with Ipilimumab and Nivolumab Therapy: Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography Findings
- PMID: 33437235
- PMCID: PMC7747087
- DOI: 10.1159/000509629
Acute Bilateral Uveitis, Hypotony, and Cataracts Associated with Ipilimumab and Nivolumab Therapy: Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography Findings
Abstract
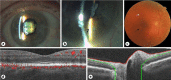
Immune checkpoint inhibitors are increasingly being used for the treatment of several malignancies. In rare cases, patients develop disabling ophthalmic side effects such as dry eyes, episcleritis, keratitis, uveitis, inflammatory orbitopathy, myasthenia gravis, macular edema, and serous retinal detachment. We present a case of acute bilateral anterior uveitis, prolonged hypotony, and cataracts following the use of dual therapy ipilimumab and nivolumab. Physicians should be aware of these immune-mediated ocular adverse events and should have a management plan to deal with these side effects that range from mild to vision threatening.
Keywords: Cataracts; Hypotony; Ipilimumab; Nivolumab; Optical coherence tomography angiography; Uveitis.
Copyright © 2020 by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Antoun J, Titah C, Cochereau I. Ocular and orbital side-effects of checkpoint inhibitors: a review article. Curr Opin Oncol. 2016 Jul;28((4)):288–94. - PubMed
-
- Abdel-Rahman O, Oweira H, Petrausch U, Helbling D, Schmidt J, Mannhart M, et al. Immune-related ocular toxicities in solid tumor patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: a systematic review. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2017 Apr;17((4)):387–94. - PubMed
-
- Dalvin LA, Shields CL, Orloff M, Sato T, Shields JA. CHECKPOINT INHIBITOR IMMUNE THERAPY: Systemic Indications and Ophthalmic Side Effects. Retina. 2018 Jun;38((6)):1063–78. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

