Minimally invasive tumor bed implant (MITBI) and peri-operative high-dose-rate brachytherapy (PHDRBT) for accelerated minimal breast irradiation (AMBI) or anticipated boost (A-PHDRBT-boost) in breast-conserving surgery for ductal carcinoma in situ
- PMID: 33437299
- PMCID: PMC7787199
- DOI: 10.5114/jcb.2020.101684
Minimally invasive tumor bed implant (MITBI) and peri-operative high-dose-rate brachytherapy (PHDRBT) for accelerated minimal breast irradiation (AMBI) or anticipated boost (A-PHDRBT-boost) in breast-conserving surgery for ductal carcinoma in situ
Abstract
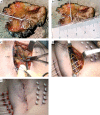
Purpose: To evaluate our institutional experience of minimally invasive tumor bed implantation (MITBI) during breast-conserving surgery (BCS) for ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) to deliver peri-operative high-dose-rate brachytherapy (PHDRBT) as accelerated minimal breast irradiation (AMBI) or anticipated boost (A-PHDRBT-boost).
Material and methods: Patients older than 40, with clinical and radiological unifocal DCIS < 3 cm were considered potential candidates for accelerated partial breast irradiation (APBI) and were implanted during BCS using MITBI-technique. Patients who in final pathology reports showed free margins and no other microscopic tumor foci, received AMBI with PHDRBT (3.4 Gy BID in 5 days). Patients with adverse features received A-PHDRBT-boost with post-operative external beam radiotherapy (EBRT).
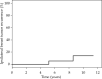
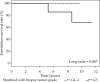
Results: Forty-one patients were implanted, and 36 were treated and analyzed. According to final pathology, 24 (67%) patients were suitable for AMBI and 12 (33%) were qualified for A-PHDRBT-boost. Reoperation rate for those with clear margins was 16.6% (6/36); this rate increased to 33% (4/12) for G3 histology, and 66% (4/6) were rescued using AMBI. Early complications were documented in 5 patients (14%). With a median follow-up of 97 (range, 42-138) months, 5-year rates of local, elsewhere, locoregional, and distant control were all 97.2%. 5-year ipsilateral breast tumor recurrence rates (IBTR) were 5.6% (2/36), 8.3% (2/24) for AMBI, and 0% (0/12) for A-PHDRBT-boost patients. Both instances of IBTR were confirmed G3 tumors in pre-operative biopsies; no IBTR was documented in G1-2 tumors. Cosmetic outcomes were excellent/good in 96% of AMBI vs. 67% in A-PHDRBT-boost (p = 0.034).
Conclusions: The MITBI-PHDRBT program allows selection of patients with excellent prognoses (G1-2 DCIS with negative margins and no multifocality), for whom AMBI could be a good alternative with low recurrence rate, decrease of unnecessary radiation, treatment logistics improvement, and over-treatment reduction. Patients whose pre-operative biopsy showed G3 tumor, presents with inferior local control and more risk of reoperation due to positive margins.
Keywords: DCIS; high-dose-rate brachytherapy; partial breast irradiation.
Copyright © 2020 Termedia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Elshof LE, Schaapveld M, Schmidt MK et al. . Subsequent risk of ipsilateral and contralateral invasive breast cancer after treatment for ductal carcinoma in situ: incidence and the effect of radiotherapy in a population-based cohort of 10,090 women. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2016; 159: 553-563. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dunne C, Burke JP, Morrow M, Kell MR. Effect of margin status on local recurrence after breast conservation and radiation therapy for ductal carcinoma in situ. J Clin Oncol 2009; 27: 1615-1620. - PubMed
-
- Morrow M, Van Zee KJ, Solin LJ et al. . Society of Surgical Oncology-American Society for Radiation Oncology-American Society of Clinical Oncology consensus guideline on margins for breast-conserving surgery with whole-breast irradiation in ductal carcinoma in situ. J Clin Oncol 2016; 34: 4040-4046. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rath MG, Uhlmann L, Heil J et al. . Predictors of residual tumor in breast-conserving therapy. Ann Surg Oncol 2015; 22: 451-458. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
