LncRNA LOC100912373 modulates PDK1 expression by sponging miR-17-5p to promote the proliferation of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 33437356
- PMCID: PMC7791483
LncRNA LOC100912373 modulates PDK1 expression by sponging miR-17-5p to promote the proliferation of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
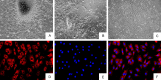
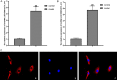
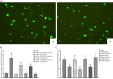
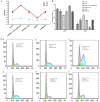
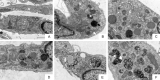
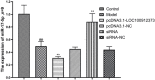
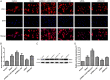
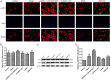
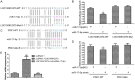
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a common autoimmune disease and characterized by chronic inflammation, abnormal synovial cell proliferation, and joint swelling and tenderness, and it causes patients substantial pain. To date, the pathogenesis of RA remains unclear, and specific treatment is still lacking in the clinic. Evidence from previous research indicated that the long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) LOC100912373 is a key lncRNA and involved in RA. However, our understanding of the specific mechanism of lncRNA LOC100912373 in RA development and progression is still in its infancy. In this study, fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLSs) were cultured by enzyme-dispersed and substrate-attached explant methods. The MTT method, flow cytometry and transmission electron microscopy were used to determine the effect of lncRNA LOC100912373 on FLSs. The expression of key genes such as lncRNA LOC100912373, miR-17-5p, PDK1 and AKT in FLSs was detected by RT-qPCR, immunofluorescence and Western blot. The localization of lncRNA LOC100912373 was determined by fluorescence in situ hybridization. The specific targeting relationship between lncRNA LOC100912373 and miR-17-5p/PDK1 was verified by RNA immunoprecipitation and luciferase reporter gene analysis. The results showed that lncRNA LOC100912373 localized in the cytoplasm and was highly expressed in the synovial tissues and FLSs of AA rats. LncRNA LOC100912373 overexpression promoted the proliferation of FLSs. In addition, lncRNA LOC100912373 could bind to miR-17-5p, and the expression of lncRNA LOC100912373 was negatively correlated with miR-17-5p and positively correlated with PDK1/AKT. In conclusion, lncRNA LOC100912373 may upregulate the expression of PDK1 by sponging miR-17-5p, accelerating the phosphorylation of AKT and inducing the proliferation of FLSs, thus promoting the occurrence and development of RA.
Keywords: Rheumatoid arthritis; ceRNA theory; fibroblast-like synoviocytes; lncRNA LOC100912373/miR-17-5p/PDK1 axis.
AJTR Copyright © 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Astragaloside regulates lncRNA LOC100912373 and the miR‑17‑5p/PDK1 axis to inhibit the proliferation of fibroblast‑like synoviocytes in rats with rheumatoid arthritis.Int J Mol Med. 2021 Jul;48(1):130. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2021.4963. Epub 2021 May 20. Int J Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34013364 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA PICSAR promotes cell proliferation, migration and invasion of fibroblast-like synoviocytes by sponging miRNA-4701-5p in rheumatoid arthritis.EBioMedicine. 2019 Dec;50:408-420. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.11.024. Epub 2019 Nov 30. EBioMedicine. 2019. PMID: 31791845 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA NEAT1 regulates the proliferation and production of the inflammatory cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes by targeting miR-204-5p.Hum Cell. 2021 Mar;34(2):372-382. doi: 10.1007/s13577-020-00461-4. Epub 2021 Jan 4. Hum Cell. 2021. PMID: 33394349
-
Influences of the lncRNA TUG1-miRNA-34a-5p network on fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLSs) dysfunction in rheumatoid arthritis through targeting the lactate dehydrogenase A (LDHA).J Clin Lab Anal. 2021 Sep;35(9):e23969. doi: 10.1002/jcla.23969. Epub 2021 Aug 17. J Clin Lab Anal. 2021. PMID: 34403518 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulation of lncRNAs in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Biomarkers, Pathogenesis and Potential Therapeutic Targets.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Mar 12;12:652751. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.652751. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33776780 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
LncRNA NORAD regulates the mechanism of the miR-532-3p/Nectin-4 axis in pancreatic cancer cell proliferation and angiogenesis.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2023 Apr 22;12(3):425-432. doi: 10.1093/toxres/tfad026. eCollection 2023 Jun. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2023. PMID: 37397924 Free PMC article.
-
The Role and Mechanism of Protein Post‑Translational Modification in Rheumatoid Arthritis.J Inflamm Res. 2025 Jul 11;18:9055-9078. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S528487. eCollection 2025. J Inflamm Res. 2025. PMID: 40666378 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluating the Role of lncRNAs in the Incidence of Cardiovascular Diseases in Androgenetic Alopecia Patients.Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2022 Jul;22(7):603-619. doi: 10.1007/s12012-022-09742-w. Epub 2022 May 4. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 35507254 Review.
-
m6A-mediated lncRNA MAPKAPK5-AS1 induces apoptosis and suppresses inflammation via regulating miR-146a-3p/SIRT1/NF-κB axis in rheumatoid arthritis.Cell Cycle. 2023 Dec-Dec;22(23-24):2602-2621. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2024.2302281. Epub 2024 Jan 16. Cell Cycle. 2023. PMID: 38225924 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomal Osteoclast-Derived miRNA in Rheumatoid Arthritis: From Their Pathogenesis in Bone Erosion to New Therapeutic Approaches.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 25;25(3):1506. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031506. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38338785 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sparks JA. Rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Intern Med. 2019;170:Itc1–Itc16. - PubMed
-
- Blum A, Adawi M. Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and cardiovascular disease. Autoimmun Rev. 2019;18:679–690. - PubMed
-
- Bystrom J, Clanchy FI, Taher TE, Mangat P, Jawad AS, Williams RO, Mageed RA. TNFα in the regulation of Treg and Th17 cells in rheumatoid arthritis and other autoimmune inflammatory diseases. Cytokine. 2018;101:4–13. - PubMed
-
- Wei XJ, Li XW, Lu JL, Long ZX, Liang JQ, Wei SB, Lu CX, Lu WZ. MiR-20a regulates fibroblast-like synoviocyte proliferation and apoptosis in rheumatoid arthritis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017;21:3886–3893. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
