Kaempferol attenuated cisplatin-induced cardiac injury via inhibiting STING/NF-κB-mediated inflammation
- PMID: 33437376
- PMCID: PMC7791507
Kaempferol attenuated cisplatin-induced cardiac injury via inhibiting STING/NF-κB-mediated inflammation
Abstract
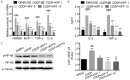
Cardiovascular complications have been well documented as the downside to conventional cancer chemotherapy. As a notable side effect of cisplatin, cardiotoxicity represents a major obstacle to the successful treatment of cancer. It has been reported that kaempferol (KPF) possesses cardioprotective and anti-inflammatory qualities. However, the effect of KPF on cardiac damage caused by conventional cancer chemotherapy remains unclear. In this study, we clarified the protective effect of KPF on cisplatin-induced heart injury, and conducted in-depth research on the molecular mechanism underlying this effect. The results showed that KPF protected against cardiac dysfunction and injury induced by cisplatin in vivo. In H9c2 cells, KPF dramatically reduced cispaltin-induced apoptosis and inflammatory response by modulating STING/NF-κB pathway. In conclusion, these results showed that KPF had great potential in attenuating cisplatin-induced cardiac injury. Besides, greater emphasis should be placed in the future on natural active compounds containing KPF with anti-inflammatory effects for the treatment of these diseases.
Keywords: Kaempferol; STING; cisplatin; inflammation.
AJTR Copyright © 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures





References
-
- El-Awady el-SE, Moustafa YM, Abo-Elmatty DM, Radwan A. Cisplatin-induced cardiotoxicity: mechanisms and cardioprotective strategies. Eur J Pharmacol. 2011;650:335–341. - PubMed
-
- Volarevic V, Markovic BS, Jankovic MG, Djokovic B, Jovicic N, Harrell CR, Fellabaum C, Djonov V, Arsenijevic N, Lukic ML. Galectin 3 protects from cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury by promoting TLR-2-dependent activation of IDO1/Kynurenine pathway in renal DCs. Theranostics. 2019;9:5976–6001. - PMC - PubMed
-
- El-Hawwary AA, Omar NM. The influence of ginger administration on cisplatin-induced cardiotoxicity in rat: light and electron microscopic study. Acta Histochem. 2019;121:553–562. - PubMed
-
- Xing JJ, Hou JG, Liu Y, Zhang RB, Jiang S, Ren S, Wang YP, Shen Q, Li W, Li XD, Wang Z. Supplementation of saponins from leaves of panax quinquefolius mitigates cisplatin-evoked cardiotoxicity via inhibiting oxidative stress-associated inflammation and apoptosis in mice. Antioxidants (Basel) 2019;8:347. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
