Pathophysiology of diabetes: An overview
- PMID: 33437689
- PMCID: PMC7791288
- DOI: 10.4103/ajm.ajm_53_20
Pathophysiology of diabetes: An overview
Abstract
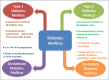
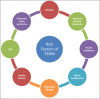
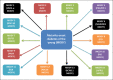
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic heterogeneous metabolic disorder with complex pathogenesis. It is characterized by elevated blood glucose levels or hyperglycemia, which results from abnormalities in either insulin secretion or insulin action or both. Hyperglycemia manifests in various forms with a varied presentation and results in carbohydrate, fat, and protein metabolic dysfunctions. Long-term hyperglycemia often leads to various microvascular and macrovascular diabetic complications, which are mainly responsible for diabetes-associated morbidity and mortality. Hyperglycemia serves as the primary biomarker for the diagnosis of diabetes as well. In this review, we would be focusing on the classification of diabetes and its pathophysiology including that of its various types.
Keywords: Diabetes mellitus; endocrinopathies; gestational diabetes; maturity-onset diabetes of the young; neonatal diabetes.
Copyright: © 2020 Avicenna Journal of Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The contributing authors have no financial or nonfinancial competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2014;37:S81–90. - PubMed
-
- American Diabetes Association. Introduction: Standards of medical care in diabetes—2018. Diabetes Care. 2018;41:S1–2. - PubMed
-
- American Diabetes Association. Microvascular complications and foot care: Standards of medical care in diabetes—2018. Diabetes Care. 2018;41:S105–18. - PubMed
-
- American Diabetes Association. Cardiovascular disease and risk management: Standards of medical care in diabetes—2018. Diabetes Care. 2018;41:S86–104. - PubMed
-
- Rawshani A, Rawshani A, Franzén S, Eliasson B, Svensson AM, Miftaraj M, et al. Mortality and cardiovascular disease in type 1 and type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2017;376:1407–18. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources